Figure 3.
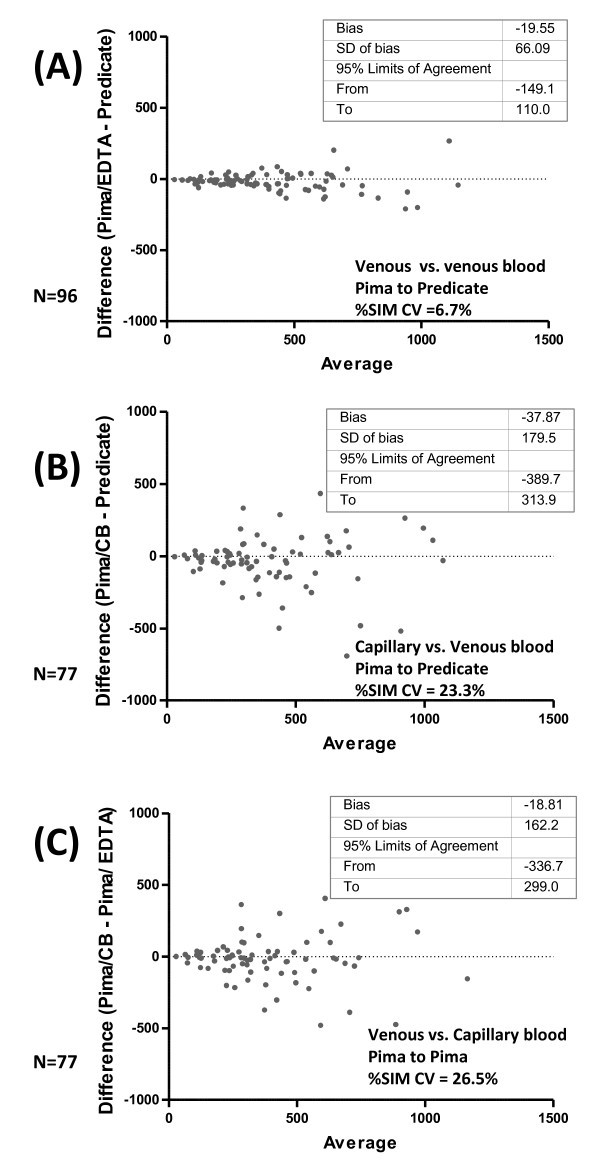
Pima™ performance with venous and capillary blood sampling. In (A), Predicate and Pima™ are both tested using venous EDTA blood, revealing excellent method agreement and small, clinically insignificant bias between systems. In (B), decreasing precision of Pima™ precision-to-predicate CD4 is noted where capillary blood sampling is used. The mean bias is within clinically acceptable limits; however, the variation noted around the mean bias is poor, with unacceptably wide LOA noted (range > 600 cells/mm3). In (C), further decreasing precision-to-predicate is revealed with even higher %SIM %CV noted in a direct Pima™ to Pima™ comparison of capillary versus venous blood. Although overall BA bias between sampling methods is clinically insignificant, the variation of this bias (reflected in the 95% LOA) is unacceptably wide, confirming the poor %SIM CV of 26.5%. Bland-Altman values shown above are cells/mm3. CB = capillary blood.
