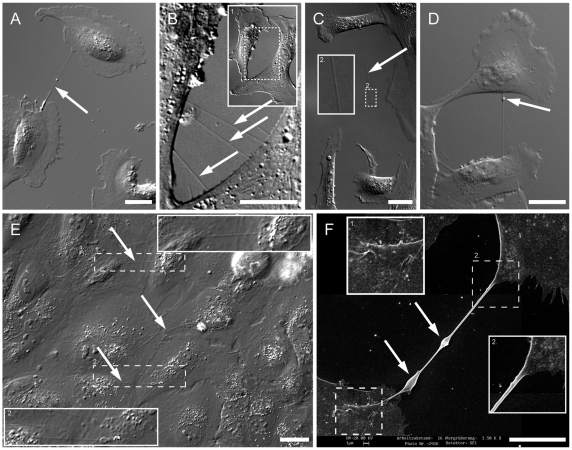
Figure 1. The presence of membrane nanotubes in live ARPE-19 cells.
(A) Two ARPE-19 cells are directly connected with a straight membrane tube (arrow). Scale bar, 20 µm. (B) High magnification of 3 separate straight membrane tubes (arrows) connecting two ARPE-19 cells. Inset 1 is an overview of the two connected cells. Scale bar, 20 µm. (C) A long nanotube (120 µm, arrow) connects ARPE-19 cells. The inset 2 shows the tube in a higher magnification. Scale bar, 20 µm. (D) A bulge (arrow) locates at the upper end of the tube. In time lapse videos the bulges moved along the tube from one cell to the other. Scale bar, 20 µm. (E) Thin membrane tubes (arrow) form and locate above the confluent layer of ARPE-19 cells after 48 h cultivation. The insets 1 and 2 show the tube in a higher magnification. Scale bar, 20 µm. (F) Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) shows the ultrastructure of a TNT between two ARPE-19 cells. Enlarged views (inset 1 and 2) show smooth membrane between the nanotube and the plasma membrane of the two connected cells. The TNT forms a straight connection between two cells and has a typical diameter of 250 nm. Arrows mark two focal thickenings of 1 µm indicating a possible transport of organelles or vesicles through the nanotube. The picture was taken with 20 kV. Scale bar, 10 µm.