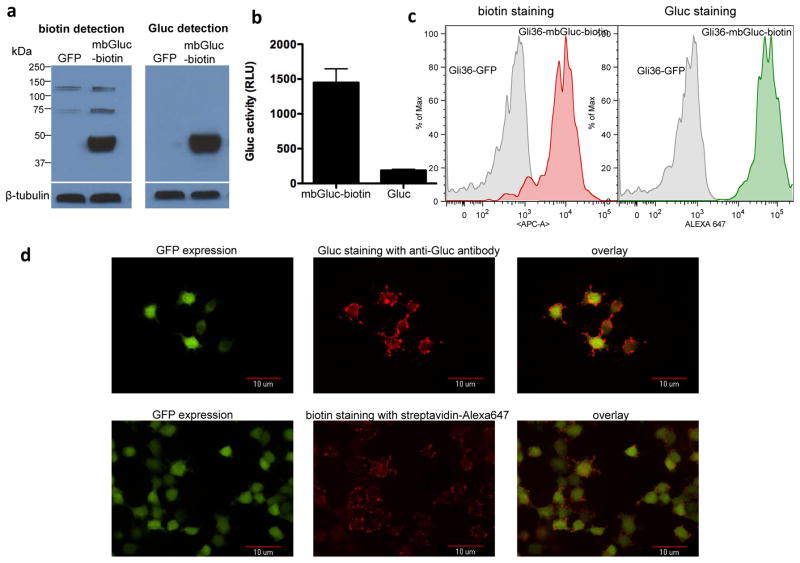
Figure 2. Analysis of cells expressing mbGluc-biotin reporter.
(a) Gli36-sshBirA cells were transduced with the lentivirus vector expressing mbGluc-biotin or GFP control. Forty-eight hours later, cells were lysed and lysates were analyzed by Western blotting for both biotinylation efficiency and Gluc expression using either streptavidin-HRP conjugate or a combination of Gluc-specific antibody followed by secondary-HRP conjugate respectively. Blots were also analyzed for β-tubulin to show equal loading. (b) Gli36 cells expressing either mbGluc-biotin or native secreted Gluc were imaged for Gluc expression on the cell surface by adding coelenterazine directly to viable cells followed by photon count using a luminometer. Data presented as average ± standard deviation (SD). (c) Viable Gli36-sshBirA cells infected with lentivirus vector encoding mbGluc-biotin and GFP or GFP alone were labeled with anti-biotin antibody conjugated to APC or Gluc antibody followed by a secondary-Alexa647 conjugate and analyzed by FACS. (d) Gli36-sshBirA cells expressing mbGluc-biotin and GFP were plated on coverslips and stained with either streptavadin-Alexa647 for biotin presentation on the cell surface (bottom pannel) or with a combination of Gluc antibody followed by secondary-Alexa647 conjugate (top pannel). Cells were then fixed using 4% paraformaldehyde and analyzed by fluorescence microscopy for both GFP expression and biotin or Gluc staining.