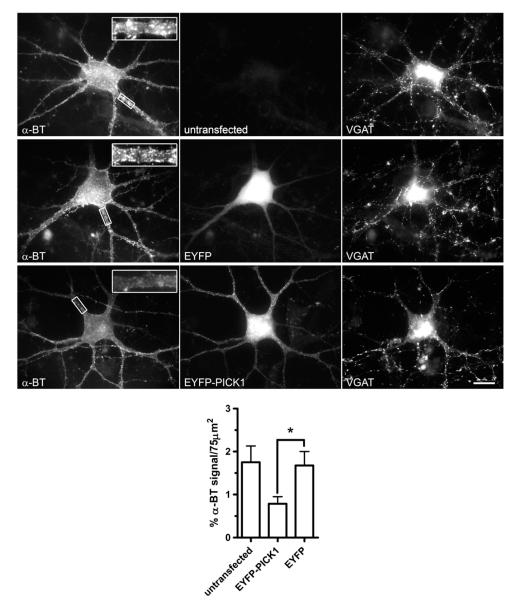
Fig. 8.
Expression of PICK1 by magnetofection causes a reduction in surface α7 nAChR clusters in cultured hippocampal interneurons. Cultured hippocampal cells were transfected with EYFP-PICK1 or EYFP constructs using magnetofection, labeled with α-BT-rhodamine and anti-VGAT antibody and analyzed by conventional fluorescence microscopy. The panels show examples of surface α7 nAChR staining by α-BT-rhodamine (left), EYFP fluorescence (middle), and VGAT staining (right) for a non-transfected control interneuron, an interneuron transfected with EYFP, and an interneuron transfected with EYFP-PICK1. PICK1 expression reduces α7 clustering. A quantitative analysis of these effects is shown at the bottom. For each neuron in a group (untransfected, EYFP-PICK1 transfected or EYFP transfected), proximal dendritic surface areas were randomly chosen (the boxes represent examples). The amount of α7 surface clusters on dendrites of transfected neurons was measured as the cumulative α-BT fluorescence area per dendritic surface area. α7 surface clustering is reduced by EYFP-PICK1 but not by EYFP in dendritic areas (*p = 0.0267; unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test). Scale bar, 20 μm.