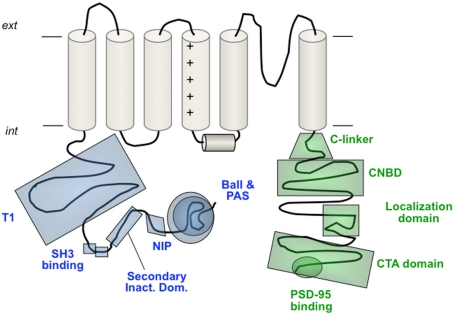
Figure 4.
Schematic view of different structural and/or functional domains recognized at the cytoplasmic ends of Kv channels. In the amino terminus these include the ball-like structure responsible for fast N-type inactivation, the eag/PAS domain of the eag-like channels, the NIP domain that protects Kv1.6 channels against rapid inactivation, the secondary inactivation domain reported for Kv1.4 channels, the double SH3 binding domain of Kv1.5, and the T1 tetramerization domain (also called NAB) of the Kv1–Kv4 channels. In the carboxy terminus the domains shown correspond to the C-linker and cNBD encountered in the eag-like channels, the localization domain and the C-terminal activation (CTA) domain of Kv2.1 and the post-synaptic density protein (PSD-95)-binding domain of some Kv1 channels. A more detailed view of the Kv7 channels carboxy terminus organization is shown schematically in Figure 6. For more explanations, see text. Note that not all the depicted domains pertain to the same Kv channel.