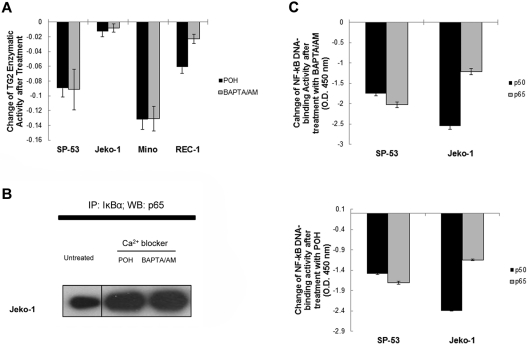
Figure 4.
Calcium blockers suppressed TG2 and NF-κB activity in MCL. (A) SP-53, Jeko-1, Mino, and REC1 cells were treated with the intracellular Ca2+ chelator BAPTA/AM (60μM for 24 hours) or the L-type calcium-channel blocker POH (1mM for 24 hours). TG2 enzymatic activity was subsequently measured using a TG2-CovTest TG2-specific colorimetric assay kit (Novus Biologicals) with cell extracts from untreated and treated SP-53 and Jeko-1 cells. Changes in TG2 enzymatic levels before and after treatment with BAPTA/AM or POH were measured. The colorimetric values in untreated samples were subtracted from the values measured in treated samples. Results are shown as the means ± SD. Treatment with the calcium blockers BAPTA/AM or POH suppressed TG2 expression in MCL cell lines. (B) Calcium blockers affected the affinity between IκBα and p65 in MCL cells. Jeko-1 cells were treated with BAPTA/AM (60μM) or POH (1mM) for 24 hours. Cell lysates were prepared from untreated and treated SP-53 and Jeko-1 cells, immunoprecipitated using an anti-IκBα Ab, and probed with an anti-p65 Ab. Equal amounts of proteins were used. The amount of p65 proteins that interacted with IκBα was increased in response to BAPTA/AM or POH treatment. IP indicates immunoprecipitation; and WB, Western blot. (C) Calcium blocker–induced TG2 inhibition suppressed NF-κB activity in MCL cells. Nuclear extracts from SP-53 and Jeko-1 cells that were untreated or treated with BAPTA/AM (60μM for 24 hours) or POH (1mM for 24 hours) were analyzed for p50 and p65 DNA-binding activities using ELISA assays. Changes in p50 and p65 DNA-binding activity levels before and after treatment with BAPTA/AM or POH were measured. The colorimetric values in untreated samples were subtracted from the values measured in treated samples. Results are shown as the means ± SD.