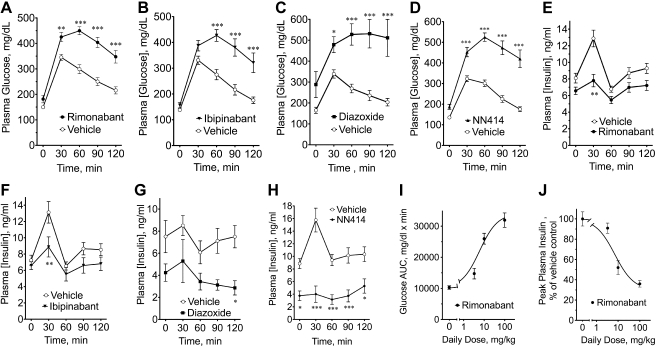
Fig. 2.
The CB1 inverse agonists rimonabant and ibipinabant and the sulfonylurea receptor 1 (SUR1)-specific ATP-sensitive potassium (KATP) channel opener NN414 exhibit acute diazoxide/NN414-like effects on plasma glucose and insulin during an oral GTT in male Zucker rats. Different cohorts of male Zucker rats received 2 daily doses of either vehicle or rimonabant (A and E) or ibipinabant (B and F; 10 mg·kg−1·day−1) 45 min before an oral GTT. C and G: diazoxide (100 mg·kg−1·day−1) or vehicle was administered with divided daily dosing: daily dose in the morning, in the afternoon, and the next morning before the GTT. D and H: NN414 (5 mg·kg−1·day−1) or vehicle was administered with divided daily dosing: ½ daily dose in the morning, ½ in the afternoon, and ½ on the morning before the GTT. Blood glucose (A–D) and plasma insulin (E–H) during the GTT are shown. Dose dependency of rimonabant on glucose area under the curve (AUC; I) and peak plasma insulin (J) during the GTTs. Data were analyzed using nonlinearizing curve-fitting software (Graphpad Prism), using single-component models. IC50s are described in the text. Body weights (g) were as follows: vehicle 457 ± 9.3, rimonabant 459 ± 19 (A and E); vehicle 466 ± 16, ibipinabant 462 ± 7.3 (B and F); vehicle 354 ± 11, diazoxide 324 ± 13 (C and G); vehicle 484 ± 12, NN414 492 ± 10 (D and H). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.