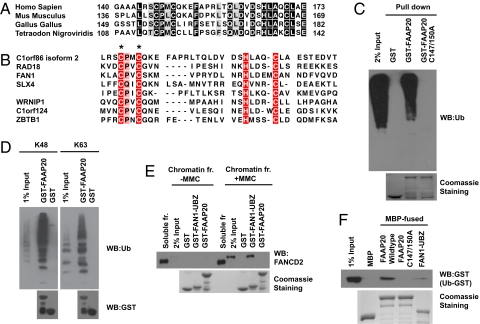
Fig. 3.
FAAP20 contains a RAD18-like UBZ domain at its C terminus. (A) Alignment of the RAD18-like UBZ domain of FAAP20 from different species. Identical residues are shaded in black. (B) Alignment of FAAP20 UBZ domain with other RAD18-like UBZ domains. The conserved Cys and His residues that define the two dyads of the ubiquitin-binding ZNF domain are shaded in red. The asterisks denote the conserved Cys147 and Cys150 residues mutated in the the FAAP20 C147/150A mutant. (C) FAAP20 binds to ubiquitin via its RAD18-like UBZ domain. GST pull-down experiments were carried out using 293T lysates and GST, GST-FAAP20, or GST-FAAP20 C147/150A mutant. Immunoblotting was conducted using anti-Ub antibody. (D) In vitro pull-down experiments were performed using K48- or K63-linked ubiquitin chains and GST-fusion proteins, as indicated. (E) Chromatin lysates were prepared from control or MMC-treated cells. In vitro pull-down experiments were performed using indicated GST-fusion proteins and Immunoblotting was conducted using anti-FANCD2 antibody. (F) FAAP20 binds to monoubiquitin. In vitro pull-down assays were performed using ub-GST and immobilized MBP-fusion proteins, as indicated.