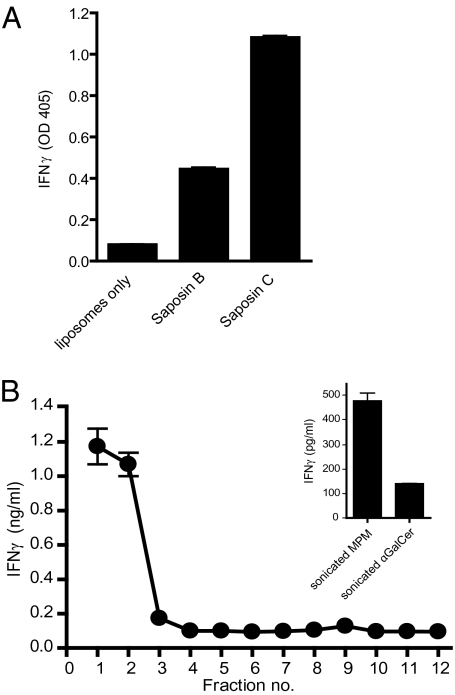
Fig. 4.
SapC facilitates CD1c-Fc lipid loading in a membrane-proximal context. (A) Lipid-transfer mediators facilitate CD1c-Fc loading. Liposomes (1 mM) with 0.1% mol MPM were incubated with saposin proteins (5.4 μM) as indicated and CD1c-Fc fusion protein in sodium citrate buffer, pH 5.0. Fusion protein samples were immobilized on protein G-coated plates. After washing with PBS solution, CD1c-restricted T cells (CD8-1 T cells) were added and incubated in complete media for 20 h. IFN-γ released by activated T cells was measured by ELISA. (B) Liposome-embedded SapC facilitates CD1c-Fc lipid loading. SapC was incubated with liposomes (1 mM total lipid) supplemented with 0.1% mol MPM in citrate buffer, pH 5.0. Liposome and SapC solutions were transferred to a sucrose gradient buffered to pH 5.0 and centrifuged at 200,000 × g. Gradient fractions were collected and dialyzed against citrate buffer, pH 5.0. CD1c-Fc fusion protein was added to each fraction and incubated. Samples were immobilized on protein G–coated plate. CD8-1 T cells (CD1c-restricted, MPM-reactive cells) were added. IFN-γ released by activated T cells was measured by ELISA. Inset: Sonicated MPM (4 μM) or αGalCer (100 ng/mL) were incubated with CD1c-Fc. After immobilization on protein G-coated plates, T cells were added to plates, and IFN-γ released by activated T cells was measured by ELISA.