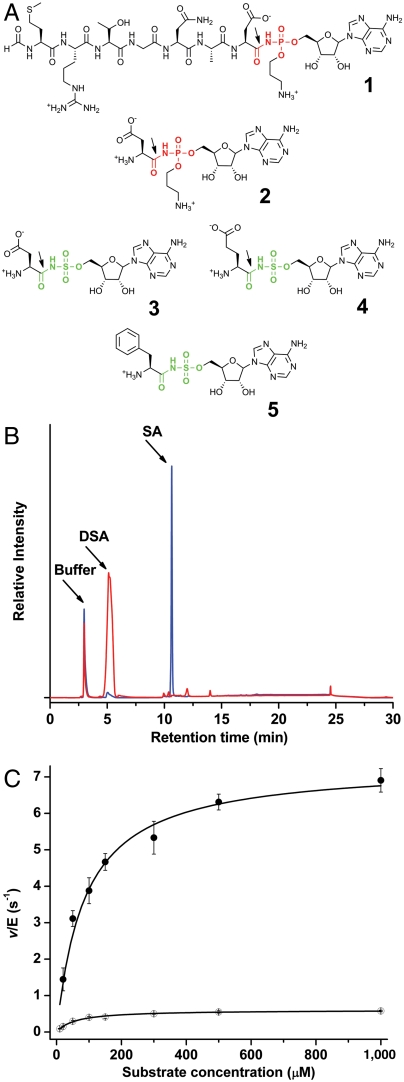
Fig. 1.
Chemical structures of microcin C7 and analogs and demonstration of MccF hydrolysis activity. (A) Chemical structures of microcin C7 (1) and its processed form (2), along with synthetic sulfamoyl adenylates of aspartate (3), glutamate (4), and phenylalanine (5). The site of hydrolysis by wild-type MccF is marked by an arrow. (B) Hydrolysis of DSA by wild-type MccF enzyme demonstrated by HPLC separation the substrate and reaction product, sulfamoyl adenosine. (C) Michaelis–Menten kinetic curves for the hydrolysis of DSA (●) and ESA (○) by wild-type MccF enzyme.