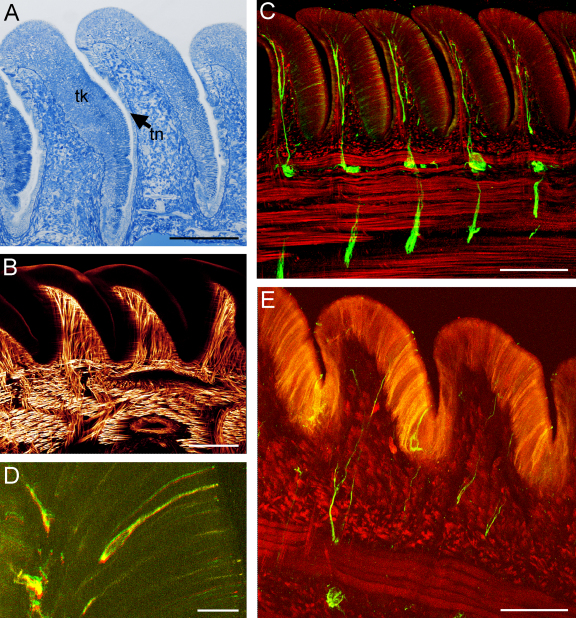
Fig. 4.
Longitudinal section of the oral ridges, light microscopy images. (A) The oral ridges of the digital tentacle are serrate and slightly concave anteriorly. The epithelium of the ridges is heterogeneous, thick (tk) on the proximal side but thin (tn) on the distal surface. Scale bar = 200 μm. (B) In the central part of the oral ridges and aboral ridges (not shown) there are large bundles of muscular fibers which fuse with the circular and longitudinal tentacle musculature. Scale bar = 150 μm. (C) Below each ridge is a sublamellar nerve plexus, interconnected with the others by a longitudinal as well as a central nerve cord. Scale bar = 150 μm. (D and E) From this plexus, nerves proceed into the ridges and end in ciliated cells on the tentacle surface. Scale bar in (D) = 15 μm, in (E) = 50 μm. Muscles were stained with phalloidin and are visualized in red; nerves were stained with acetylated α-tubulin and show up in green (D and E) or yellow (C).