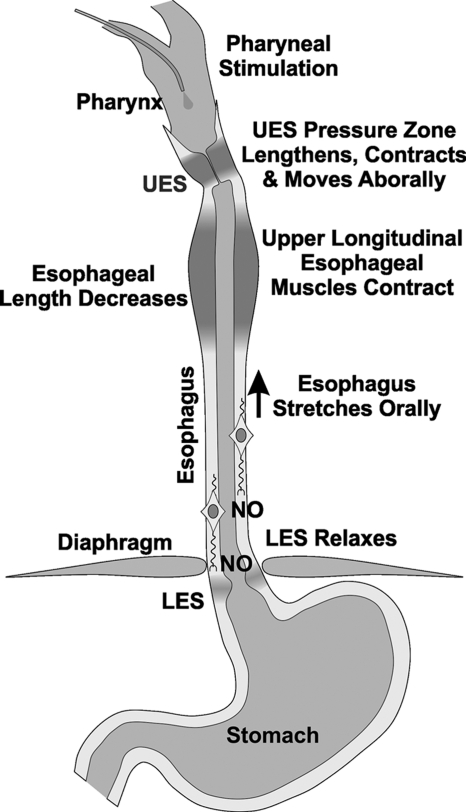
Fig. 7.
Schematic of the effects of subthreshold pharyngeal stimulus on the esophagus and LES. A subthreshold pharyngeal stimulus induces contraction of the longitudinal muscle of the proximal esophagus, which we propose activates stretch sensitive inhibitory motor neurons of the esophagus and LES to release nitric oxide (NO) to induce relaxation of the esophagus and lower esophageal sphincter.