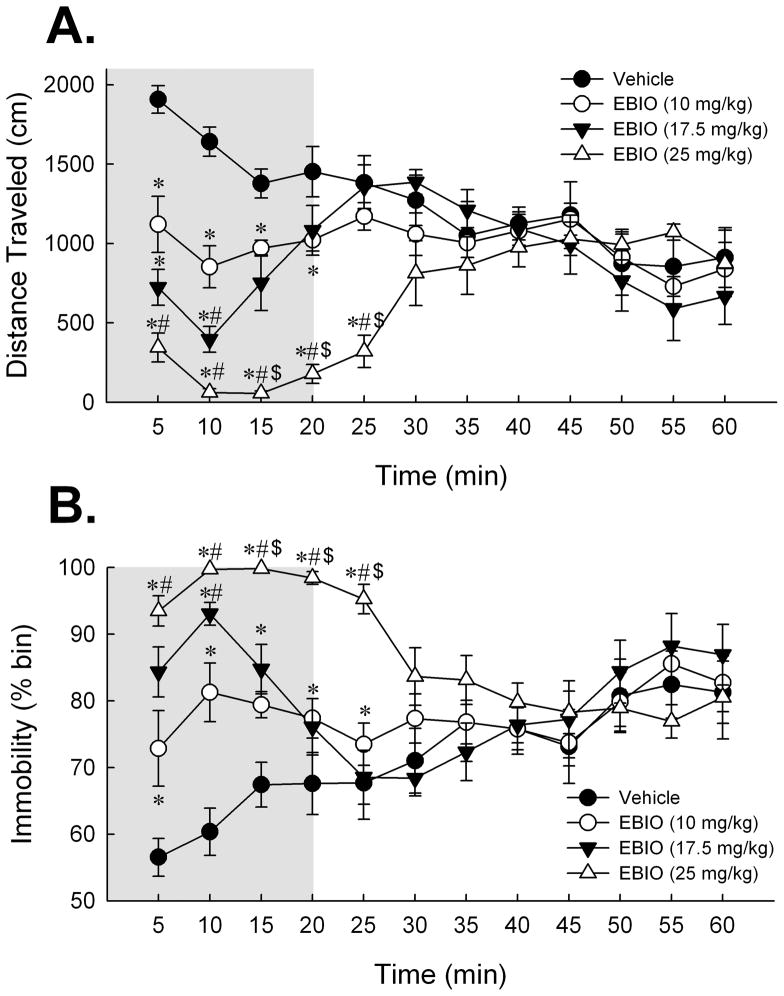
Figure 1.
Activation of SK channels with systemic EBIO depresses locomotor responding in C57BL/6NHsd mice. (A) Dose-dependent effect of EBIO on mean distance traveled in the 60 min period in the open field expressed as cm traveled per 5-min time bin. Post-hoc Tukey HSD tests revealed that mice treated with EBIO exhibited a significant decrease in distance traveled during the first 15 min of the session. Exploratory motor activity recovered to the level of the 1% DMSO vehicle group by 20 min in the 10 and 17.5 mg/kg EBIO-treated mice and by 30 min in the 25 mg/kg EBIO-treated mice. (B) Dose-dependent effect of EBIO on immobility over the 60 min period expressed as percent of time deemed immobile by the Ethovision software per 5-min time bin. Post-hoc Tukey HSD tests revealed that measures of immobility recovered to vehicle levels within 20 min for the 10 and 17.5 mg/kg dose groups and by 30 min for the 25 mg/kg dose group. Shaded region depicts the 20 min post-injection interval over which all doses of EBIO impaired exploratory motor behavior in mice. In light of this effect, a 20 min delay was imposed after EBIO administration and before behavioral testing for all subsequent experiments. Error bars are SEM. *, P < 0.05 vs. vehicle; #, P < 0.05 vs. 10 mg/kg EBIO; and $, P < 0.05 vs. 17.5 mg/kg EBIO. Vehicle, n = 8; 10 mg/kg EBIO, n = 8; 17.5 mg/kg EBIO, n = 8; 25 mg/kg EBIO, n = 7.