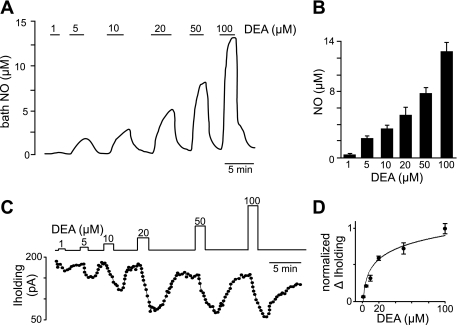
Fig. 1.
Nitric oxide (NO) measurements and estimated diethylamine (DEA) EC50 values of hypoglossal motoneurons in vitro. NO was measured in the tissue bath using a polarographic electrode (+860 mV) with a tip diameter of 30 μm. A trace of NO concentration (A) and summary data (B) show that bath NO concentration increased fairly linearly with increasing concentrations of DEA. C: a trace of holding current (Iholding) from a hypoglossal neuron shows that exposure to this same range of DEA concentrations reversibly decreased holding current. D: average (n = 5) change (Δ) in holding current at each DEA concentration was normalized and plotted as a dose-response curve. The estimated DEA EC50 of hypoglossal motoneurons was ∼18 μM.