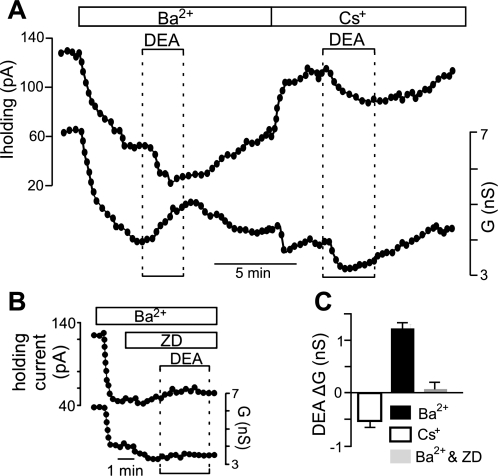
Fig. 4.
NO modulation of hypoglossal motoneurons involves activation of an inward Cs+-sensitive current and inhibition of an outward Ba2+-sensitive current. A: traces of holding current (Iholding) and conductance (G) show that Ba2+ (2 mM) decreased holding current and conductance. In the continued presence of Ba2+, exposure to DEA (20 μM) decreased holding current and increased conductance. A second exposure to DEA, this time in Cs+ (2 mM), decreased holding current and conductance. G, conductance. B: in the presence of Ba2+ to block background K+ channels and ZD-7288 (ZD; 50 μM) to block HCN channels, exposure to DEA had no effect on holding current or conductance. C: summary data showing DEA-induced conductance (ΔG) in Ba2+ (n = 10), Cs+ (n = 25), and Ba2+ plus Cs+ or ZD (n = 8). These results suggest that effects of NO on motoneurons involve inhibition of a background K+ channel and activation of a Cs+-sensitive Ih-like current.