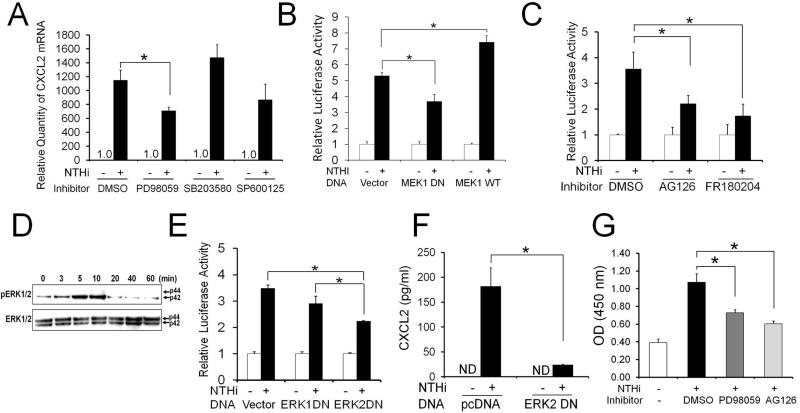
FIGURE 3.
MEK1-ERK2 signaling is required for NTHi-induced activation of c-Jun resulting in CXCL2 up-regulation in SLFs. A, Quantitative RT-PCR analysis shows that NTHi-induced CXCL2 up-regulation is inhibited by PD98059, a MEK inhibitor, not by other MAPK inhibitors. B, Luciferase assays demonstrate that a dominant-negative inhibition of MEK1 suppresses NTHi-induced CXCL2 up-regulation, but is enhanced by the over-expression of the wild type of MEK1. Vector: a mock transfection. C, NTHi-induced CXCL2 up-regulation is noted to be inhibited by AG126 and FR180204. D, Phosphoylation assays shows that the SLFs activates ERK in response to NTHi, peaked around 10 min after exposure. Note that ERK2 (p42), not ERK1 (p44), is mainly phosphorylated upon exposure to NTHi in the SLFs. E, Luciferase assays show that NTHi-induced CXCL2 up-regulation is suppressed by a dominant-negative inhibition of ERK2, but not by ERK1. F, ELISA analysis shows that a dominant-negative inhibition of ERK2 significantly suppresses NTHi-induced CXCL2 up-regulation. ND: not detected. pcDNA: a mock transfection. G, Transcription factor ELISAs show that NTHi-induced activation of c-Jun is inhibited by PD98059 and AG126. OD: optical density. Results were expressed as fold-induction, taking the value of the non-treated group as 1. The experiments were performed in triplicate and repeated twice. Values are given as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). *: p < 0.05.