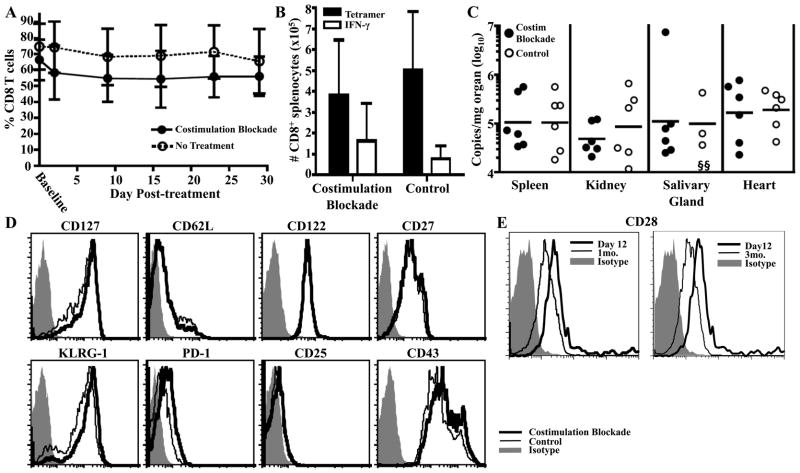
Figure 5.
Q9:VP2.139-specific cells do not depend on costimulation for maintenance. B6.Kb−/−Db−/− mice were infected with MPyV and 3 mo p.i. given a cocktail of MR-1 (α-CD40L) and CTLA-4-Ig weekly for 1 mo. Control infected mice received no Ab. A. Frequency (± SD) of Q9:VP2.139-specific CD8 T cells in blood over time. Baseline indicates frequency before start of treatment. B. Number (± SD) of splenic Q9:VP2.139-specific CD8 T cells was determined by tetramer staining and VP2.139 peptide-stimulated intracellular anti-IFN-γ staining after 1 mo of treatment. C. Number of MPyV genome copies was determined by qPCR in indicated organs after 1 mo of treatment. Each point corresponds to an individual mouse, and horizontal lines indicate geometric mean. D. Expression of indicated surface molecule by CD8+ Q9:VP2-139-specific splenocytes after 1 mo of treatment. E. CD28 expression on Q9:VP2.139-specific CD8 T cells in MPyV-infected B6.Kb−/−Db−/− mice at the indicated time post-infection. Data are representative of six mice per group pooled from two independent experiments. The limit of detection of this assay is 20 copies of genomic viral DNA. §, sample is below the limit of detection.