Figure 1. MPO activity and LTB4 production in the lungs is dependent on CXCL1 during K. pneumoniae infection.
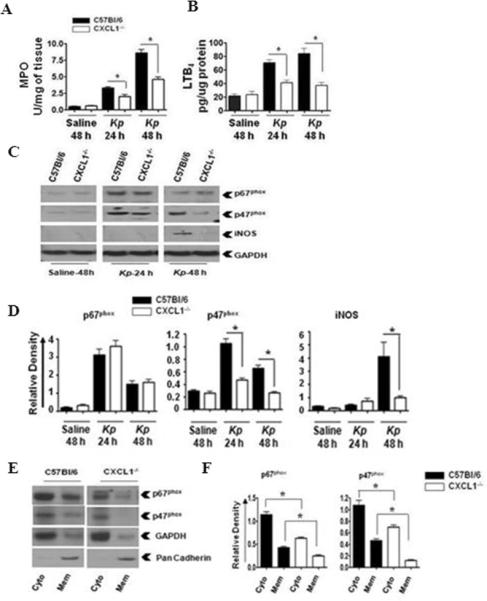
MPO activity (A) and LTB4 levels (B) in homogenized (unlavaged) whole lungs of WT (C57Bl/6) and CXCL1-/- mice infected with K. pneumoniae (103 CFU/mouse) for 24 and 48 h. Data are presented as means ± SEM. n=6-8 mice/group. (* indicates p<0.05 compared with CXCL1-/- mice). The levels of p67phox, p47phox, and iNOS (C) in K. pneumoniae-infected homogenized whole lungs of WT and CXCL1-/- mice at 24 and 48 h post-infection. The blot is representative of three individual blots with identical results. Densitometric analysis of p67phox, p47phox and iNOS expression (D) in homogenized lungs. Densitometry was performed from three separate blots. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. n=6-8 mice/group. (* indicates p<0.05 compared to CXCL1-/- mice). Levels of p67phox and p47phox in cytosolic and membrane fractions of the lung (E) upon K. pneumoniae infection. This is a representative blot of three independent experiments. GAPDH is a cytosolic marker, pan-cadherin is a plasma membrane marker. Densitometric analysis of p67phox and p47phox levels (F) in cytosol and membrane fractions of the lung following K. pneumoniae infection. Protein expression was quantitated from three separate blots. Data are shown as means ± SEM. For experiments E-F, a total of 6-8 mice were used in each group. (* indicates p<0.05 as compared to CXCL1-/- mice.)
