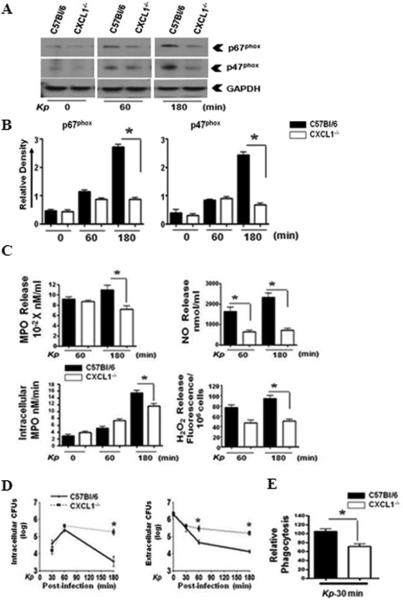
Figure 3. CXCL1 is essential for Klebsiella-induced expression of p67phox, p47phox, and ROS/RNS production by neutrophils.
Levels of p67phox and p47phox (A) in bone marrow-derived neutrophils from WT and CXCL1-/- mice after infection with K. pneumoniae (MOI of 1). This is a representative blot from three separate experiments. Densitometric analysis from three separate blots (B) shows the expression of p67phox and p47phox in K. pneumoniae stimulated-neutrophils that were normalized against GAPDH. (* indicates p<0.05 as compared to CXCL1-/- neutrophils). MPO activity and nitrite and H2O2 release (C) in WT and CXCL1-/- neutrophils stimulated with K. pneumoniae. The levels of MPO, nitrite, and H2O2 were measured in infected neutrophils at 30, 60, and 180 min post-infection. Experiments were performed in triplicates. Bacterial killing capacity (D) of K. pneumoniae-infected neutrophils from WT and CXCL1-/- deficient mice was determined by assessing extracellular and intracellular CFUs at 30, 60, and 180 mins post-infection with K. pneumoniae (MOI of 1). Relative phagocytosis (E) of K. pneumoniae-infected WT and CXCL1-/- neutrophils at 30 min post-treatment (MOI of 1). For experiments A-E, a total of 5-8 mice/group were used. (* indicates p<0.05 compared with CXCL1-/- neutrophils).