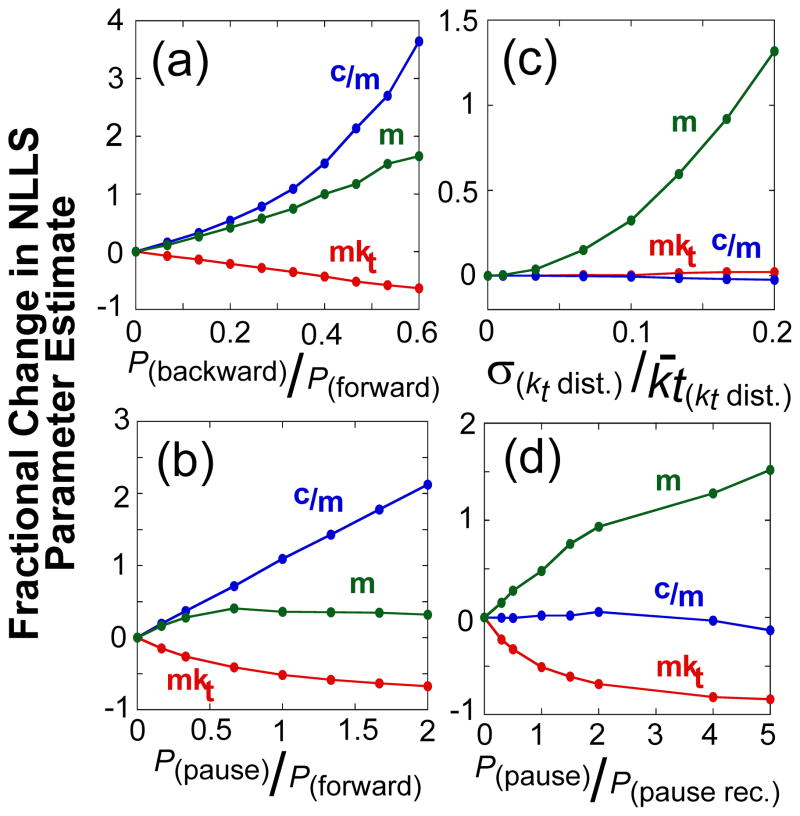
Figure 5.
The dependence of the estimates of kinetic parameters for DNA translocation on the presence of slipping, pausing, and static disorder in the translocase population. Simulated translocation time courses with translocase pausing, slipping, and static disorder were analyzed with the n-step model (see Materials and Methods). The data are plotted as the fractional change in the value of the fit parameter determined in the presence of the kinetic heterogeneity from the value determined in the absence of the kinetic heterogeneity as a function of the ratio of specific probabilities used in the simulations, unless otherwise noted: macroscopic translocation rate (mkt, red), ATP coupling stoichiometry (c/m, blue), and kinetic step size (m, green). (A)- The effect of backward motion. (B)- The effect of pausing with futile ATP hydrolysis. (C)- The effect of a distribution of inter-enzyme translocation rates (static disorder). The fractional change in the fit parameter is plotted as a function of the ratio of the standard deviation of the distribution to its mean. (D)- The effect of random pauses of varying duration. Here the probability of pausing was kept constant, equal to the probability of stepping forward, but the probability of recovering from the paused varied. The fractional change in the fit parameter is plotted as a function of the ratio of the probability of pausing to the probability of recovering from the pause.