Table 1.
Variables, parameters and abbreviations in the salmon louse model.
| symbol | definition (units) |
|---|---|
| F | number of farm fish in the area |
| P | total number of lice on farmed fish in the area |
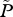 |
average abundance of lice per farmed fish, P/F |
| L | number of free-living copepodites from lice on farmed fish |
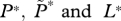 |
equilibrium values of 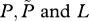 , respectively , respectively |
| L0 | number of free-living copepodites from lice on wild fish |
| μ | louse mortality rate not caused by treatment of harvest (one per day) |
| Tg | grow-out time (farmed fish harvest rate is 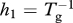 ) (days) ) (days) |
| h = h1 + h2 | louse mortality rate from harvest and treatment, respectively (one per day) |
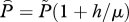 |
scaled louse abundance used in §5. |
| γ | mortality rate of free-living copepodites (one per day) |
| β | transmission coefficient (captures per copepodite per host per unit time) |
| λ | natality (copepodites produced per adult female louse per unit time) |
| ψ | settlement success (probability an attached copepodite survives to adult) |
| λ0, ψ0, μ0, γ0, β0, h0 | reference values for λ, ψ, μ, γ, β, h, respectively |
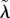 |
scaled parameter (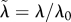 ), and similarly for ), and similarly for 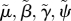
|
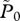 |
the limit of 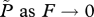 at reference values ( at reference values (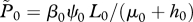 ) ) |
| Fx | critical stocking level, given by equation (3.2) |
| Fx0 | Fx evaluated at λ0, ψ0, μ0, β0, γ0, h0 |
| S | salinity in parts per thousand (‰) |
| θ | temperature in °C |
| aμ, aγ, aβ, aλ, aψ | salinity coefficients of μ, γ, β, λ, ψ (1/‰) |
| bμ, bγ, bβ, bλ, bψ | temperature coefficients of μ, γ, β, λ, ψ (1/°C) |
| gm, gstd | geometric mean and standard deviation |
| G | weight of market fish (kg) |
| Kx | critical production level (kT yr–1) |
