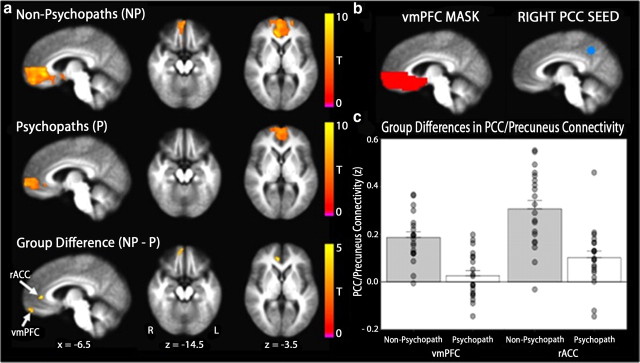
Figure 3.
Functional connectivity between medial parietal cortex and vmPFC is reduced in psychopaths. a, Mean precuneus/PCC–vmPFC connectivity maps are depicted separately for non-psychopaths and psychopaths on the group mean anatomical image, thresholded at a cluster corrected p < 0.05. Scale bars indicate the uncorrected t statistic. Both groups exhibit significant resting connectivity between right precuneus/PCC and regions of vmPFC. The group difference map indicates two separate clusters within vmPFC where non-psychopaths have significantly greater connectivity with the precuneus/PCC seed than psychopaths (vmPFC: x = −12, y = −51, z = −12, cluster size = 27 voxels; rACC: x = −9, y = −39, z = +6, cluster size = 15 voxels). b, Group differences in connectivity were assessed in the vmPFC mask (red) for correlation coefficients computed using the mean time series extracted from the PCC seed (blue; x = −5, y = +49, z = +40). c, The bar plots depict group differences in connectivity estimates (Fisher z-transformed correlation coefficients) within each significant cluster. Error bars indicate SEM. Filled circles represent values from individual subjects.