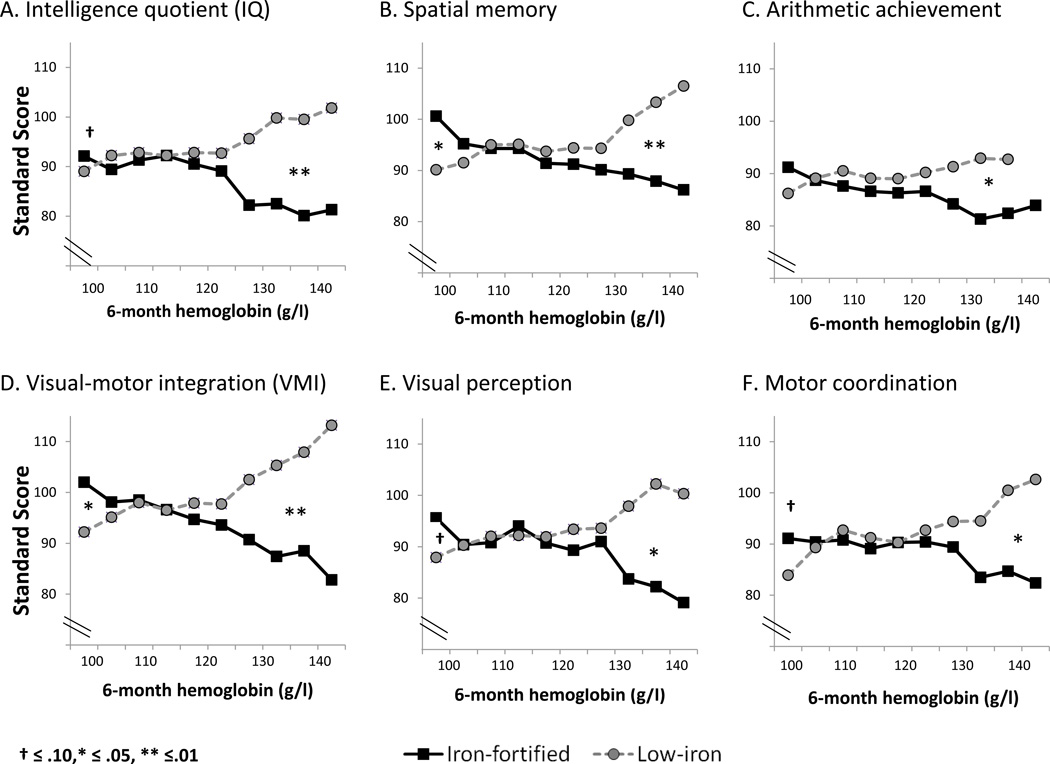
Figure 2.
Developmental outcomes at 10 years and the interaction between 6-month HB and iron-fortified vs. low-iron infant formula. The HB distribution is truncated at the low end by the criterion for anemia at 6 months; 34 capillary values ≤ 100 g/l are not shown since venous HB was higher. The pattern was better outcome with iron-fortified formula for children with the lowest HB and worse outcome for those with the highest HB. Cut points of about 105 g/l and 128 g/l were determined empirically by sensitivity analyses; the significance of test-score differences was based on covaried regression analysis controlling for gender and gestational age. Ns for the high and low HB cut points for each test are found in Table 3.