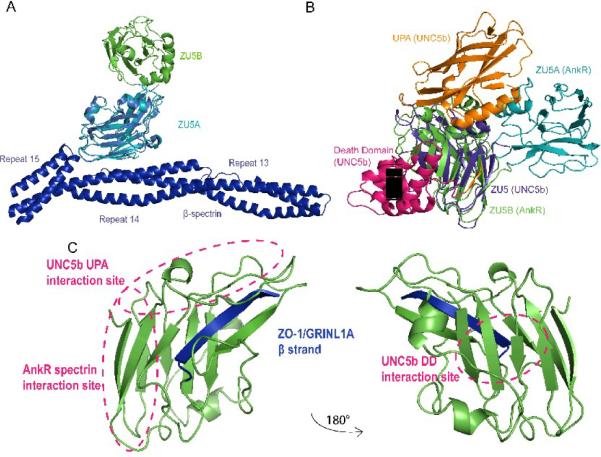
Figure 5. The ZU5 domain is a versatile protein interaction module.
A. Superposed structures of the ZU5A domain in ZU5A-ZU5B on the ZU5A in complex with spectrin. Ribbon diagram of the ZU5A-ZU5B (turquoise, green) structure superposed on the ZU5A domain (red) of the complex with β-spectrin (blue)24. The diagram shows that ZU5B is unlikely to interact with spectrin as it is found away from the spectrin/ankyrin interface. This finding is supported by biochemical experiments that show that the ZU5B domain does not alter the binding characteristics significantly. B. Superposed structures of the ZU5A-ZU5B fragment of ankyrin-R on the UNC5b supramodule. Ribbon diagram of the ZU5A-ZU5B fragment (turquoise, green) superposed on the UNC5b supramodule comprising the ZU5, UPA and DD domains25. The ZU5 domain of UNC5b (pink) was superposed on the ankyrin-R ZU5B domain. The superposition shows that the ankyrin DD domain could interact in a similar manner without any major conformational changes. The UPA domain could also interact with ZU5B in a similar manner, although there are some potential clashes in the superposed structures. Some of these potential clashes may not exist as they involve a region in the UNC5b UPA domain that is not present in ankyrin. Finally, the ankyrin ZU5A domain clashes with the UNC5b UPA domain, suggesting that a small reorientation of the ZU5A domain may be needed for proper interaction. Overall, the superposition shows that a similar supramodule could be formed in ankyrin and that this supramodule is not likely to interact directly with spectrin. C. The ZU5 domain has several distinct binding surfaces. The ZU5 domain can use different regions to interact with different proteins. The known areas of interaction are marked, showing the different, non-overlapping areas of the ZU5 domain involved in different complexes. Furthermore, the incorporation of additional β strands can also serve as a mechanism for interaction, as observed in the interaction with the DD domain in UNC5b25 and the GRINL1A peptide in ZO-132.