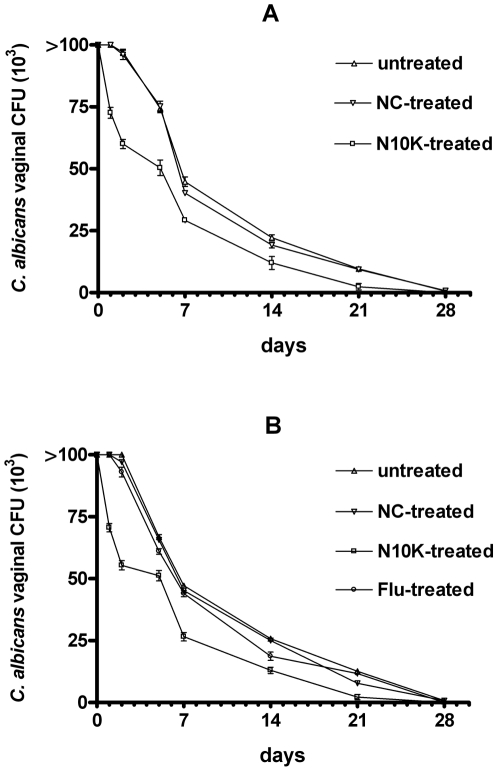
Figure 3. Protection conferred by N10K upon mice intravaginally infected with fluconazole-susceptible strain SA40 (panel A) and fluconazole-resistant strain AIDS68 (panel B) of C. albicans.
All mice (five per group) were given 106 cells in 20 µl of saline solution on day 0 and were sampled for initial intravaginal colony forming units (CFU). The therapeutics (N10K, 20 µg, i.e. 18 µM; negative control peptide, NC, 20 µg; and fluconazole, Flu,100 µg) were administered 1, 24, and 48 h postchallenge. On days 1, 2, 5, 7, 14, and 21, all the differences in the CFU vaginal counts between N10K-treated and control groups (untreated and NC-treated) were statistically significant (P<0.001). The differences in vaginal CFU counts between N10K-treated and fluconazole-treated AIDS68-infected animals were statistically significant (P<0.001 all days except P<0.01 day 14) on the same days. The statistical significance was assessed by the analysis of variance (ANOVA) and the Bonferroni post hoc test. Data are from one of two experiments performed with similar results.