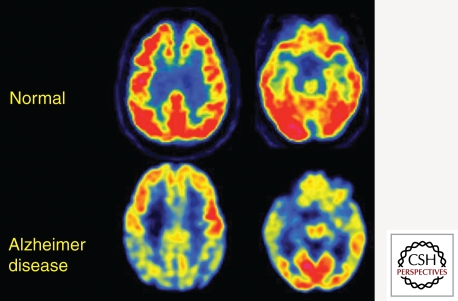
Figure 3.
Transaxial FDG-PET images of a normal control subject and a patient with mild AD. Note severe hypometabolism (yellow and blue cortical regions) in association and limbic cortex. These are the typically involved brain regions that define the FDG endophenotype of AD. They include posteriomedial parietal (precuneus), lateral parietal, lateral temporal, and medial temporal lobes. This pattern slowly worsens in parallel with symptoms and is well correlated at autopsy with AD pathologic diagnosis.