Abstract
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
Enhancement of GABAergic function is the primary mechanism of important therapeutic agents such as benzodiazepines, barbiturates, neurosteroids, general anaesthetics and some anticonvulsants. Despite their chemical diversity, many studies have postulated that these agents may bind at a common or overlapping binding site, or share an activation domain. Similarly, we found that flavan-3-ol esters act as positive modulators of GABAA receptors, and noted that this action resembled the in vitro profile of general anaesthetics. In this study we further investigated the interactions between these agents.
EXPERIMENTAL APPROACH
Using two-electrode voltage clamp electrophysiological recordings on receptors of known subunit composition expressed in Xenopus oocytes, we evaluated positive modulation by etomidate, loreclezole, diazepam, thiopentone, 5α-pregnan-3α-ol-20-one (THP) and the flavan-3-ol ester 2S,3R-trans 3-acetoxy-4′-methoxyflavan (Fa131) on wild-type and mutated GABAA receptors.
KEY RESULTS
The newly identified flavan, 2S,3S-cis 3-acetoxy-3′,4′-dimethoxyflavan (Fa173), antagonized the potentiating actions of Fa131, etomidate and loreclezole at α1β2 and α1β2γ2L GABAA receptors. Furthermore, Fa173 blocked the potentiation of GABA responses by high, but not low, concentrations of diazepam, but did not block the potentiation induced by propofol, the neurosteroid THP or the barbiturate thiopental. Mutational studies on ‘anaesthetic-influencing’ residues showed that, compared with wild-type GABAA receptors, α1M236Wβ2γ2L and α1β2N265Sγ2L receptors are resistant to potentiation by etomidate, loreclezole and Fa131.
CONCLUSIONS AND IMPLICATIONS
Fa173 is a selective antagonist that can be used for allosteric modulation of GABAA receptors. Flavan-3-ol derivatives are potential ligands for etomidate/loreclezole-related binding sites at GABAA receptors and the low-affinity effects of diazepam are mediated via the same site.
Keywords: GABAA receptors, Xenopus oocytes, GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid), flavonoids, flavans, anaesthetic agents, sedative effects, α1-containing GABAA receptors
Introduction
GABA type A (GABAA) receptors are ligand-gated chloride channels consisting of a heteropentameric assembly of proteins derived from a family of 19 genes, namely α1–6, β1–3, γ1–3, δ, π, ε, θ and ρ1–3 (Simon et al., 2004). Common topography of these subunits is a large extracellular amino-terminal domain, four transmembrane segments (TM1–TM4) and a long intracellular domain between TM3 and TM4. The chloride channel is delimited by the second transmembrane domain of each of the five subunits, with the large extracellular domain constituting the agonist/antagonist orthosteric binding sites (McKernan and Whiting, 1996; Miller and Smart, 2010). In addition, the receptor contains a variety of allosteric sites that can modulate its function by altering the energy barrier required for conformational changes in the chloride channel (Johnston, 2005). Many important therapeutic agents such as benzodiazepines, barbiturates, loreclezole, and general anaesthetics like etomidate and propofol bind to these allosteric sites to produce an enhancement of GABAA receptor function.
Functional GABAA channels require the presence of α and β subunits, but the vast majority of naturally expressed receptors also contain a γ subunit (McKernan and Whiting, 1996). Interestingly, agents such as barbiturates, neurosteroids, loreclezole and etomidate can positively modulate αβ type receptors, suggesting that their corresponding binding sites lie within one of these subunits, or their interface (Malherbe et al., 1990; Thompson et al., 1996; Rudolph and Antkowiak, 2004; Belelli and Lambert, 2005). Furthermore, while the presence of a γ subunit is necessary for high-affinity modulation by benzodiazepine ligands, later studies proved that these drugs can also exert low-affinity (µM) modulation of αβ GABAA receptors (Stevenson et al., 1995; Walters et al., 2000). Although much evidence suggests the presence of discrete binding sites for these agents, many reports also suggested a common mechanism or overlapping sites. For example, mutational studies have identified a glycine at position 219 on the second transmembrane domain of the β2 subunit as fundamental for anaesthetic modulation of GABA currents (Chang et al., 2003). These authors found a linear correlation between the volume of the amino acid at this position and the loss of modulation by etomidate, propofol, pentobarbital and alphaxalone. Similarly, modulation by etomidate, propofol and loreclezole can be greatly reduced when the N265 residue at β-TM2 is replaced by serine, indicating a common mechanism. This position, however, seems to have little influence on the modulation by barbiturates and neurosteriods (Wingrove et al., 1994; Belelli et al., 1997; 1999; Siegwart et al., 2003; Desai et al., 2009). Also, several mutational studies at M286 on β-TM3 demonstrated its relevance for both propofol and etomidate modulatory activity, although modulation by loreclezole, neurosteroids and barbiturates remained unaffected (Krasowski et al., 1998; Siegwart et al., 2003).
Similarly, the contribution of the α subunit to anaesthetic action has been examined by site-directed mutagenesis. For example, Drafts and Fisher (2006) found that the mutation T69K in α6 subunit reduced both pentobarbital and etomidate agonist action, and mutations in α-TM1 alter sensitivity to neurosteroids (Hosie et al., 2006; Akk et al., 2008). Li and colleagues (2006) utilized a radiolabelled photoreactive etomidate analogue to identify residues involved in the binding of etomidate. Their results pointed not only at the previously mentioned M286 in β2-TM3, but also at M236 in α1-TM1 (and the homologous methionines in α2,3,5), an amino acid not previously implicated in the binding of this anaesthetic. Later functional studies revealed that substitution of this residue by a bulky amino acid such as tryptophan significantly reduces the modulation elicited by etomidate, but not by alphaxalone or pentobarbital (Stewart et al., 2008).
Studies involving site-directed mutagenesis intrinsically carry the paradox of whether the mutated residue being studied is directly involved in ligand–protein interactions, or is involved in the allosteric changes taking place as a consequence of the binding process, making the results difficult to interpret. Whereas the use of techniques such as photoaffinity labelling, radioligand binding competition or the simple use of specific antagonists may provide a deeper insight into unravelling the mysteries of these potentially overlapping binding sites. We have previously described a series of flavan-3-ol derivatives as positive modulators of GABAA receptors (Fernandez et al., 2008; Mewett et al., 2009). The derivative 2S,3R-trans 3-acetoxy-4′-methoxyflavan (Fa131) demonstrated positive allosteric properties over a range of GABAA subunit combinations, and in particular had a higher efficacy at α2-containing GABAA receptors. We noted at the time that the mode of action of Fa131 resembled that of other GABAA modulators such as neurosteroids, barbiturates and anaesthetics such as etomidate. In this present study, we carried out mutational studies on ‘anaesthetic-influencing’ residues to test their role in flavan-elicited modulation of GABAA receptors. Furthermore, we discovered a new flavan derivative, namely 2S,3S-cis 3-acetoxy-3′,4′-dimethoxyflavan (Fa173), featuring antagonist properties. Fa173 is the first reported ligand to inhibit the modulation of GABA by etomidate, loreclezole, diazepam and flavans, but not thiopentone or 5α-pregnan-3α-ol-20-one (THP), indicating that these drugs may share a common binding pocket or activation domain.
Methods
DNA constructs and ligands
cDNA for human α1, β2 and γ2L GABAA receptor subunits subcloned into pCDM8 were provided by Dr Paul Whiting (Merck, Sharpe and Dohme Research Labs, Harlow, UK). The protocol for in vitro transcription of cRNA has been described previously (Hall et al., 2005). Briefly, cDNA vectors were linearized with the appropriate restriction endonucleases and capped transcripts were produced from linearized plasmids using the mMessage mMachine T7 transcription kit (Ambion, Austin, TX, USA). cRNA was diluted and stored in diethylpyrocarbonate-treated water at −80°C until use. Site-specific mutations were introduced into the cDNAs of the GABAA receptor subunits using QuikChange site-directed mutagenesis kit (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA, USA). Mutagenic oligonucleotides used were (5′ to 3′): β2N265S, ACAATCAGCACCCACCTCAGGGAAAC; α1M236A, CCTGCCGTGCATAGCGACAGTTATTCTC; α1M236W, CCTGCCGTGCATATGGACAGTTATTCTC. Mutant clones were submitted to complete sequencing to corroborate the successful incorporation of the point mutation and absence of spurious mutations.
Fa131 and Fa173 >99% purity (Figure 1) were synthesized in our laboratories as previously described (Mewett et al., 2009). Diazepam was purchased from Apin Chemicals Ltd. (Oxon, UK), sodium thiopental was from Jurox (Rutherford, NSW, Australia), loreclezole and etomidate [(R)-1-(1-phenylethyl)-1H-imidazole-5-carboxylic acid ethyl ester] were from Tocris (Ellisville, MO, USA). Propofol was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St Louis, MO, USA). THP ((3α,5β)-3-hydroxy-pregnan-20-one) was kindly provided by Dr Peter Burden, Department of Pharmacology, University of Sydney.
Figure 1.
Molecular structure of the compounds utilized in the study.
Two-electrode voltage-clamp recordings from Xenopus oocytes
Recombinant receptors were expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes; the nomenclature used to identify these receptor types conform to the British Journal of Pharmacology's Guide to Receptors and Channels (Alexander et al., 2011). The procedure for the harvesting and enzymatic separation of Xenopus laevis oocytes was identical to that described previously (Hall et al., 2005; Fernandez et al., 2008) and was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of the University of Sydney. Briefly, female X. laevis were anaesthetized by immersion in 0.17% 3-aminobenzoic acid ethyl ester with 0.02% NaCl for 10–15 min, and a lobe of the ovaries was surgically removed. The lobe was rinsed with oocyte releasing buffer 2 (OR2; 82.5 mM NaCl, 2 mM KCl, 1 mM MgCl2.6H2O, 5 mM HEPES, pH 7.5) and treated with collagenase A (2 mg·mL−1 in OR2, Boehringer Manheim, Germany) for 2 h to separate oocytes from connective tissue and follicular cells. Released oocytes were rinsed in ND96 wash solution (96 mM NaCl, 2 mM KCl, 1 mM MgCl2.6H2O, 1.8 mM CaCl2, 5 mM HEPES, pH 7.5). Stage V–VI oocytes were injected (Nanoject, Drummond Scientific Co., Broomall, PA, USA) with a total of 3–5 ng of cRNA. When expressing receptors containing a γ subunit, a 1:1:2 ratio of α : β : γ subunits was used. After the injection, oocytes were incubated at 16°C in ND96 storage solution (96 mM NaCl, 2 mM KCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 1.8 mM CaCl2, 5 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, supplemented with 2.5 mM pyruvate, 0.5 mM theophylline and 50 µg·mL−1 gentamycin) for 2 days before use in electrophysiological studies.
Currents were recorded using the two-electrode voltage clamp technique as previously described (Walters et al., 2000; Hall et al., 2005). Oocytes were individually placed in a 100 µL chamber connected to a reservoir bottle containing ND96 solution (96 mM NaCl, 2 mM KCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 1.8 mM CaCl2, 5 mM HEPES, pH 7.5). Glass microelectrodes were made using a micropipette puller (Narishige Scientific Instrument Laboratory, Tokyo, Japan) and filled with 3 M KCl (0.5–2 MΩ). The oocytes were impaled and the membrane potential was clamped at −60 mV while continuously superfused with ND96 solution (10 mL·min−1). Stock solutions of the drugs were prepared in dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO), except for GABA and sodium thiopental where distilled water was used, and applied into the perfusate until a peak response was reached. DMSO concentration in the perfusate was 0.6% and did not produce any alteration in the recording. Voltage clamp experiments were conducted using a Geneclamp 500 amplifier (Axon Instruments Inc., Foster City, CA, USA). Current amplitudes were calculated off-line using Chart software v3.6 (ADInstruments, NSW, Australia).
Responses to GABA applications were normalized as I% = (I/Imax), where I is the peak amplitude of current response and Imax is the maximal current produced by GABA measured in each individual cell. Modulation of GABA-elicited currents was tested by co-applying increasing concentrations of the drugs with a concentration of GABA that produced 3% of maximal activation (EC3, determined for each cell). Current responses were recorded and normalized as: fractional potentiation = (Idrug−IGABA) / IGABA, where Idrug is the current in the presence of a given concentration of drug, and IGABA is the amplitude of the control GABA current. Finally, experiments involving the antagonist Fa173 were conducted by co-applying GABA EC3, the positive modulator at a concentration that produced 50% its maximal effect (EC50, determined for each cell), and increasing concentrations of Fa173. Data were normalized according to the equation: % inhibition: 100 × (Imod−Ianta) / (Imod−IGABA), where Ianta is the response in the presence of Fa173, IGABA is the response to GABA alone and Imod is the response to GABA plus positive modulator. In all cases, a 3–5 min washout period was allowed between drug applications to avoid receptor desensitization. Normalized responses were pooled and graphed as mean ± SEM from at least two different batches of injected oocytes. Responses were fitted to the four-parameter logistic equation: I = Imax / (1 + (EC50 / [A])nH), where I is the peak amplitude of the current elicited by a given concentration of agonist [A], Imax is the maximum amplitude of the current, EC50 is the concentration required for half-maximal response, and nH is the Hill coefficient (Prism v5 GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA). Best-fit parameters were first compared by extra-sum-of-squares F-test to detect whether an estimated parameter differs among data sets. Individual differences between best-fit values were detected by non-overlapping confidence intervals. All data analyses were conducted using Prism v5 and a P value lower than 0.05 was considered of statistical significance.
Results
Mutational analysis of β2-N265 and α1-M236
The co-injection of mRNA encoding point-mutated subunits of the GABA receptor type A resulted in functional GABA-activated channels. The potency of GABA to activate α1β2N265Sγ2L receptors was slightly lower compared with wild-type, but this change was not statistically significant (Table 1). Conversely, receptors containing a tryptophan point mutation on methionine 236 (α1M236Wβ2γ2L) were more sensitive to GABA activation as revealed by a significantly lower EC50 (Table 1). Interestingly, when the same residue was substituted by an alanine, which is much smaller in size, no significant changes in GABA activation were observed (Table 1). To test for spontaneous channel opening, we applied picrotoxin alone at 1 mM concentration to all receptor types. Interestingly, only α1M236Wβ2γ2L receptors showed an upward change in baseline, representing about 3–6% of maximal GABA-induced activation (data not shown).
Table 1.
Estimated parameters from best-fit to four-parameter logistic equation for GABA activation and positive modulation by Fa131, etomidate, loreclezole, thiopental to wild-type and mutated GABAA receptors
| Drug/receptor type | Maximal fractional effecta | EC50 | Hill coefficient | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GABA | ||||
| α1β2γ2L | 1.02 ± 0.06 | 36.2 ± 4.8 | 1.0 ± 0.2 | 10 |
| α1β2 | 0.95 ± 0.04 | 5.9 ± 1.1** | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 7 |
| α1β2N265Sγ2L | 1.01 ± 0.04 | 63.6 ± 5.5 | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 7 |
| α1M236Wβ2γ2L | 1.04 ± 0.05 | 8.5 ± 0.9* | 0.73 ± 0.07 | 4 |
| α1M236Aβ2γ2L | 1.02 ± 0.02 | 46.7 ± 3.2 | 0.80 ± 0.04 | 4 |
| Fa131 | ||||
| α1β2γ2L | 14.7 ± 0.6 | 9.7 ± 1.7 | 1.9 ± 0.6 | 5 |
| α1β2 | 10.2 ± 1.2 | 7.5 ± 1.2 | 2.1 ± 0.9 | 6 |
| α1β2N265Sγ2L | 6.0 ± 0.2*** | 18.1 ± 1.7*** | 1.6 ± 0.2 | 5 |
| α1M236Wβ2γ2L | 7.0 ± 0.6*** | 4.6 ± 1.3 | 1.3 ± 0.5 | 6 |
| α1M236Aβ2γ2L | 13.3 ± 0.9 | 12.5 ± 3.7 | 2.3 ± 0.9 | 4 |
| Etomidate | ||||
| α1β2γ2L | 28.9 ± 1.9 | 3.2 ± 1.0 | 1.5 ± 0.5 | 6 |
| α1β2 | 33.6 ± 2.1 | 7.5 ± 1.2 | 2.1 ± 0.7 | 4 |
| α1β2N265Sγ2L | 18.1 ± 1.1* | 22.0 ± 5.0*** | 1.6 ± 0.4 | 5 |
| α1M236Wβ2γ2L | 18.0 ± 0.9* | 14.2 ± 2.1*** | 1.4 ± 0.2 | 5 |
| α1M236Aβ2γ2L | 32.8 ± 1.2 | 5.7 ± 0.9 | 1.3 ± 0.2 | 4 |
| Loreclezole | ||||
| α1β2γ2L | 9.5 ± 0.9 | 9.8 ± 2.1 | 2.2 ± 1.1 | 5 |
| α1β2 | 7.4 ± 0.8 | 11.3 ± 1.1 | 1.8 ± 0.6 | 4 |
| α1β2N265Sγ2L | 3.0 ± 0.5** | 24.0 ± 3.8* | 1.6 ± 0.6 | 5 |
| α1M236Wβ2γ2L | 6.1 ± 0.6* | 9.3 ± 1.9 | 1.4 ± 0.4 | 4 |
| α1M236Aβ2γ2L | 8.7 ± 0.7 | 12.0 ± 3.5 | 2.1 ± 0.7 | 4 |
P < 0.05;
P < 0.01
P < 0.001; significantly different compared to value at corresponding wild-type receptor.
Note that the normalization method differs between GABA-alone dose-response curves and potentiation by positive modulators.
The flavan-3-ol derivative Fa131 potentiated GABA-elicited currents at both α1β2γ2L and α1β2 wild-type GABAA receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Similarly, the anaesthetic etomidate and the anticonvulsant loreclezole elicited a positive modulatory action on these receptor types in a way resembling the effect of Fa131. Corresponding EC50 values for the modulation of GABA currents at both receptor subtypes were in the low micromolar range for all three drugs, and corresponding concentration-response curves presented high Hill coefficient values.
Point mutation of the 265 serine residue on β2-TM2 proved to form functional channels that exhibited a substantial resistance to the modulatory action of Fa131. Representative current traces depicting this effect are shown in Figure 2A, where the potentiating action of Fa131 (10 µM) is shown at different receptor subunit combinations. Fa131 can potentiate the GABA EC3 10 times at this concentration at α1β2γ2L wild-type GABAA receptors; however, this enhancement was reduced to three times at α1β2N265Sγ2L. Full concentration-response curves are shown in Figure 2A right panel. The Fa131 EC50 was shifted from 9.7 to 18.1 µM, while the maximal potentiation was reduced to half, compared with wild-type, both effects reaching statistical significance (Table 1). Similarly, the methionine-to-tryptophan substitution at position 236 in α1-TM1 had drastic, but unequal effects on the potentiation induced by this drug. A concentration of 10 µM Fa131 only potentiated GABA currents five times in this case (Figure 2A), and while the EC50 was slightly shifted to the left (4.6 µM), the maximal enhancement was significantly lowered from 14.7 to 7 times the GABA EC3 (Figure 2A and Table 1). Finally, replacing this same residue by an alanine induced no significant changes in the modulatory action of Fa131 over GABA-elicited currents (Table 1).
Figure 2.
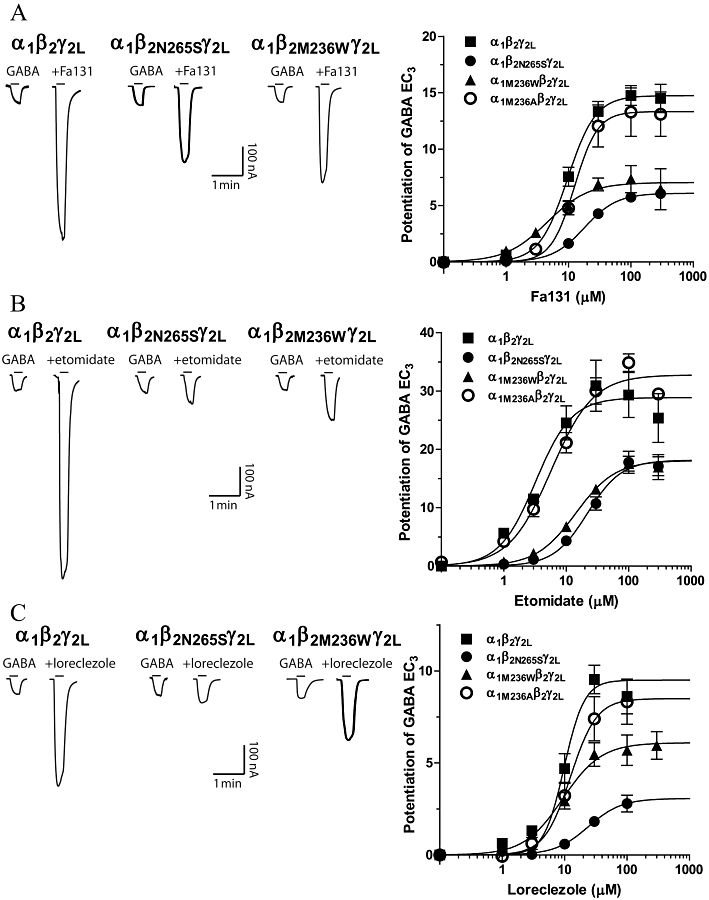
Potentiation of GABA current responses by Fa131 (A) and etomidate (B) and loreclezole (C) at α1β2γ2L, α1β2N265Sγ2L, α1M236Wβ2γ2L and α1M236Aβ2γ2L GABAA receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Left panels show currents traces (nA vs. min) illustrating the enhancing effects of these drugs at different receptor types. Horizontal bars represent drug application. GABA alone corresponds to EC3, determined for each oocyte expressing each subunit combination, and was approximately 5 µM (α1β2γ2L), 7 µM (α1β2N265Sγ2L), 0.2 µM (α1M236Wβ2γ2L) and 3 µM (α1M236Aβ2γ2L). Current traces shown correspond to 10 µM Fa131, 3 µM etomidate and 10 µM loreclezole application. Right panels are full concentration-response curves for the potentiating effects of these drugs on GABA-elicited currents, at each receptor subtype. Data points represent mean ± SEM (n ≥ 4) of peak current response normalized as described in Methods. Data were fitted using four-parameter logistic equation and the best-estimated values for each parameter are detailed in Table 1.
In oocytes expressing wild-type α1β2γ2L GABAA receptors, etomidate induced a significant potentiating effect, enhancing GABA EC3 more than 20 times at 3 µM (Figure 2B). Both N265S in β2-TM2 and M236W in α1-TM1 mutations substantially impaired the etomidate modulatory action, with 3 µM etomidate having virtually no effect on α1β2N265Sγ2L receptors, and only enhancing GABA currents two times at α1M236Wβ2γ2L (Figure 2B). Concentration-response curves for etomidate at both mutated receptors were significantly shifted to the right (Figure 2B right panel). Changes in potency were characterized by a significant increase in etomidate EC50 from 3.2 µM at wild-type receptors to 22.0 and 14.2 µM at α1β2N265Sγ2L and α1M236Wβ2γ2L receptors, respectively (Table 1). Similarly, maximal potentiation induced by this drug was significantly lowered from 28.9 times the GABA EC3 response at wild-type receptors, to approximately 18 times at each of the mutated receptors (Table 1). However, mutation M236A at α1-TM1 presented no significant changes on etomidate-induced potentiation (Figure 2B, Table 1).
The anticonvulsant loreclezole also potentiates the GABA response at wild-type α1β2γ2L GABAA receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes; 10 µM loreclezole induced a clear enhancement of GABA currents (six times the GABA EC3) as depicted in current traces shown in Figure 2C. The point-mutation N265S at β2 completely abolished the potentiation by 10 µM loreclezole (Figure 2C), and produced a significant shift-to-the-right in its concentration-response curve (Figure 2C right panel). Consequently, the EC50 for this drug increased from 9.8 µM at wild-type receptors to 24.0 µM at α1β2N265Sγ2L receptors, while the maximal effect achieved decreased from 9.5- to 3-fold potentiation (Table 1). In contrast, the mutation M236W at α1-TM1 had less pronounced effects on loreclezole potentiation; 10 µM loreclezole potentiated the corresponding GABA EC3 by three times at α1M236Wβ2γ2L receptors, compared with the sixfold potentiation in wild-type receptors (Figure 2C). The concentration-response curves for loreclezole presented a similar EC50 value at both receptor subtypes, while the maximal potentiation significantly decreased from 9.5 times to 6.1 times at α1M236Wβ2γ2L receptors (Table 1). As seen with Fa131 and etomidate, mutation of the methionine 236 at α1-TM1 to an alanine did not affect the modulatory action of loreclezole (Figure 2C, Table 1).
Fa173 is a neutral modulator and antagonizes the modulatory action of flavans
The flavan analogue Fa173 (100 µM) was inactive when applied in the absence of GABA and showed no significant modulatory effects on GABA-elicited (EC3–5 and ECmax) currents at α1β2 or α1β2γ2L receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Current traces shown in Figure 3A illustrate the lack of significant effects of Fa173 (1–300 µM) over corresponding GABA EC3 concentrations at these two receptor subunit combinations. Only at very high concentrations, 100 and 300 µM, some weak potentiation of GABA EC3 was evident. This effect reached approximately 20% enhancement over the corresponding GABA-elicited current response (Figure 3B).
Figure 3.
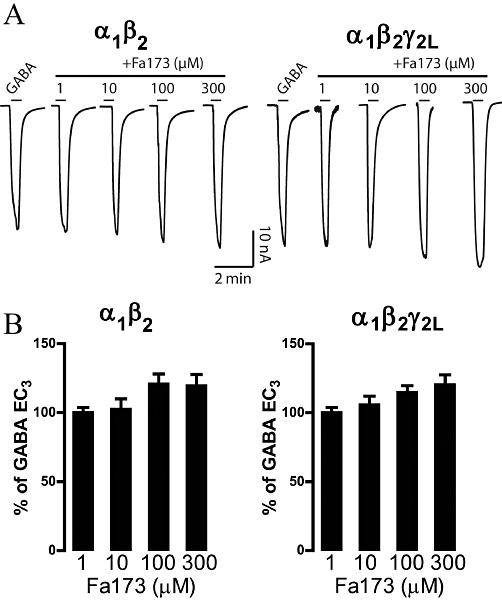
Co-application of GABA and the flavan derivative Fa173 at both α1β2 and α1β2γ2L GABAA receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. (A) Current traces illustrating the effect that Fa173 exerts over GABA-elicited currents. Only at very high concentrations Fa173 weakly potentiated GABA responses at both receptor subtypes. GABA applications were 1 µM and 5 µM, at α1β2 and at α1β2γ2L, respectively, equivalent to their corresponding EC3. Horizontal bars represent drug application. (B) Histograms depict the percentage of current potentiation over the current response elicited by GABA alone. Columns represent mean ± SEM peak current response (n = 6).
In turn, Fa173 was able to dose-dependently reduce the potentiation of GABA currents induced by Fa131 at both α1β2γ2L and α1β2 GABAA receptors (Figure 4A,B respectively). For these experiments, we selected a low concentration of GABA (EC3), and combined it with a concentration of Fa131 that produces half its maximal potentiation response (EC50). We then co-applied these two drugs with increasing concentrations of Fa173 and recorded the final current peak amplitude. Representative current traces of these experiments are depicted in Figure 4A,B. Concentration-response curves for Fa173 inhibitory action over Fa131 potentiation at both receptor subtypes are shown in Figure 4C. Fa173 was equipotent at both receptor subunit combinations (IC50 = 11.4 ± 0.9 µM at α1β2γ2L and 7.8 ± 1.2 µM at α1β2), and similarly, its neutralizing efficacy was comparable (maximal inhibition = 100 ± 5% and 93 ± 5%, respectively, Figure 4C).
Figure 4.
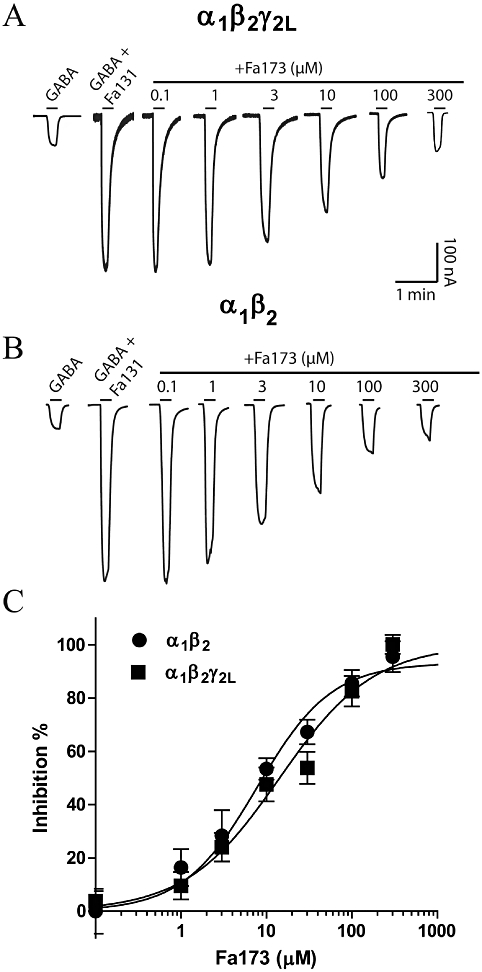
The flavan Fa173 acts as an antagonist of the GABAA positive modulator Fa131 at both α1β2γ2L and α1β2 recombinant receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Current traces (nA vs. min) illustrating the concentration-dependent blockade that Fa173 exerts over the potentiating action of Fa131 at (A) α1β2γ2L and (B) α1β2 receptors. Drug concentrations were 5 µM GABA and 15 µM Fa131 at α1β2γ2L and 1 µM GABA and 10 µM Fa131 at α1β2, equivalent to their corresponding EC3 and EC50, respectively. Horizontal bars represent drug application. (C) Concentration-response curve for Fa173 antagonistic action over Fa131-induced potentiation of GABA currents at both receptor subtypes. Data points represent mean ± SEM peak current response normalized as described in Methods. Data were fitted using four-parameter logistic equation and the best-estimated values for each parameter are: IC50 = 11.4 ± 0.9 µM, maximal inhibition = 100 ± 5%, n = 7 at α1β2γ2L; IC50 = 7.8 ± 1.2 µM, maximal inhibition = 93 ± 5%, n = 6 at α1β2. Hill coefficient values were not different from unity and are not reported.
Fa173 antagonizes the potentiation induced by etomidate and loreclezole, but not by propofol, THP or thiopental
Considering the ability of Fa173 to antagonize the potentiating effects of Fa131, we tested its antagonistic profile over a series of well-known GABAA positive modulators. Thus, etomidate, propofol, loreclezole, the neurosteroid THP and the barbiturate thiopental were selected to conduct antagonism experiments. Assays were carried out by co-applying GABA (EC3) plus modulator (EC50) and Fa173 (increasing concentrations), in order to estimate an inhibitory potency for the antagonist.
Fa173 similarly neutralized the potentiating effects of etomidate at α1β2 and α1β2γ2L GABAA receptors (Figure 5A,B). Representative current traces shown in Figure 5A,B depict the potentiation induced by etomidate of the GABA EC3 response, and its subsequent blockade by increasing concentrations of Fa173. The potency of Fa173 to antagonize etomidate was comparable at both receptor subunit combinations (IC50 = 12.0 ± 1.1 µM and 6.1 ± 1.3 µM, at α1β2γ2L and α1β2 receptors, respectively), as was its maximal inhibitory effect (maximal inhibition = 86 ± 8% and 81 ± 5%, respectively) (Figure 5C).
Figure 5.
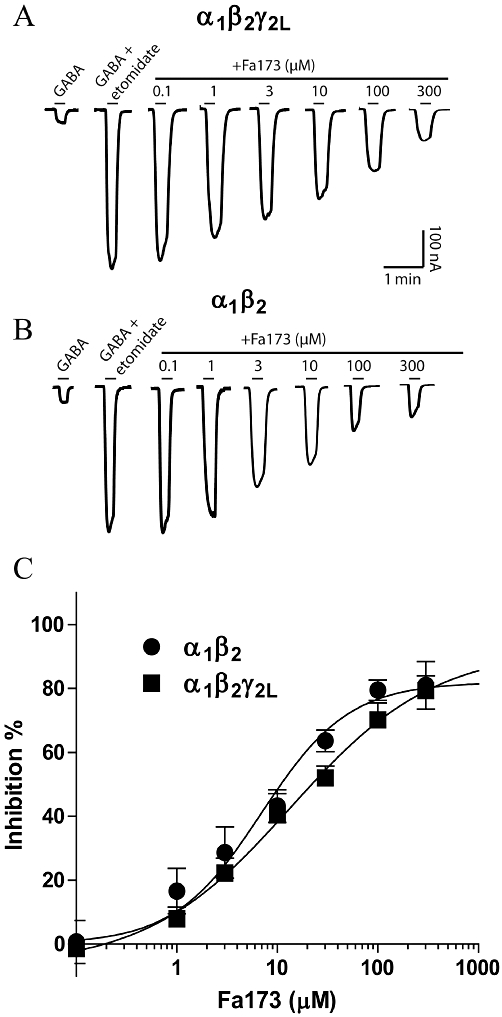
The flavan Fa173 acts as an antagonist of the etomidate-induced enhancement of GABA currents. (A) Current traces (nA vs. min) illustrating the blockade that increasing concentrations of Fa173 exert over the potentiating action of etomidate at α1β2γ2L receptors. (B) Current traces (nA vs. min) illustrating the blockade that increasing concentrations of Fa173 exert over the potentiating action of etomidate at α1β2 receptors. Drug concentrations were 3 µM GABA and 10 µM etomidate at α1β2γ2L and 1 µM GABA and 10 µM etomidate at α1β2, equivalent to their corresponding EC3 and EC50, respectively. Horizontal bars represent drug application. (C) Concentration-response curves for Fa173 blockade of etomidate-induced potentiation (IC50 = 12.0 ± 1.1 µM and 6.1 ± 1.3 µM, maximal inhibition = 86 ± 8% and 81 ± 5%, at α1β2γ2L and α1β2 receptors, n = 6 and 5, respectively).
Loreclezole can also induce large potentiation of GABA-elicited currents at both at α1β2 and α1β2γ2L GABAA receptors (Figure 6). This enhancement was antagonized by co-applying increasing concentrations of the antagonist Fa173, as depicted in the current traces shown in Figure 6A,B. At α1β2γ2L receptors, the IC50 was 6.6 ± 0.2 µM with a maximal inhibition of 99 ± 11%, while at α1β2 the IC50 was 3.8 ± 0.9 µM with a maximal inhibition of 94 ± 4% (Figure 6C).
Figure 6.
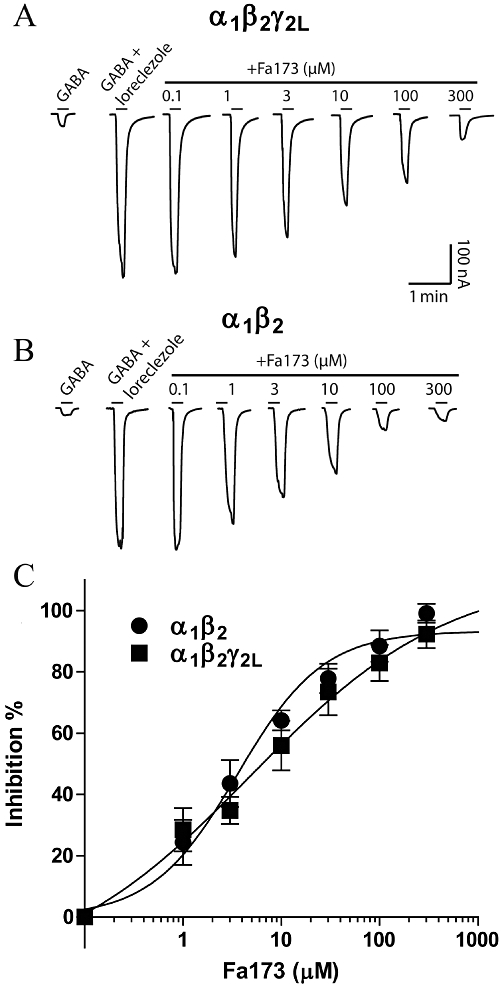
The flavan Fa173 acts as an antagonist of the loreclezole-induced enhancement of GABA currents. (A) Current traces (nA vs. min) illustrating the blockade that increasing concentrations of Fa173 exert over the potentiating action of loreclezole at α1β2γ2L receptors. (B) Current traces (nA vs. min) illustrating the blockade that increasing concentrations of Fa173 exert over the potentiating action of loreclezole at α1β2 receptors. Drug concentrations were 3 µM GABA and 10 µM loreclezole at α1β2γ2L and 1 µM GABA and 10 µM loreclezole at α1β2, equivalent to their corresponding EC3 and EC50, respectively. Horizontal bars represent drug application. (C) Concentration-response curves for Fa173 blockade of loreclezole-induced potentiation (IC50 = 6.6 ± 0.2 µM and 3.8 ± 0.9 µM, maximal inhibition = 99 ± 11% and 94 ± 4%, n = 7 and 5, at α1β2γ2L and α1β2 receptors, respectively).
The antagonizing properties of Fa173 were tested against the positive modulatory action of THP, thiopental and propofol at α1β2 and α1β2γ2L GABAA receptors (n = 4) (Figure 7). Fa173 (1–100 µM) failed to alter the enhancement of the GABA response induced by THP (Figure 7A) or by thiopental (Figure 7B), at both receptor subtypes. Finally, Fa173 (60 µM) also failed to alter the enhancement of the GABA response induced by propofol (10 µM) at α1β2 and α1β2γ2L receptors (n = 3) (Figure 7C).
Figure 7.
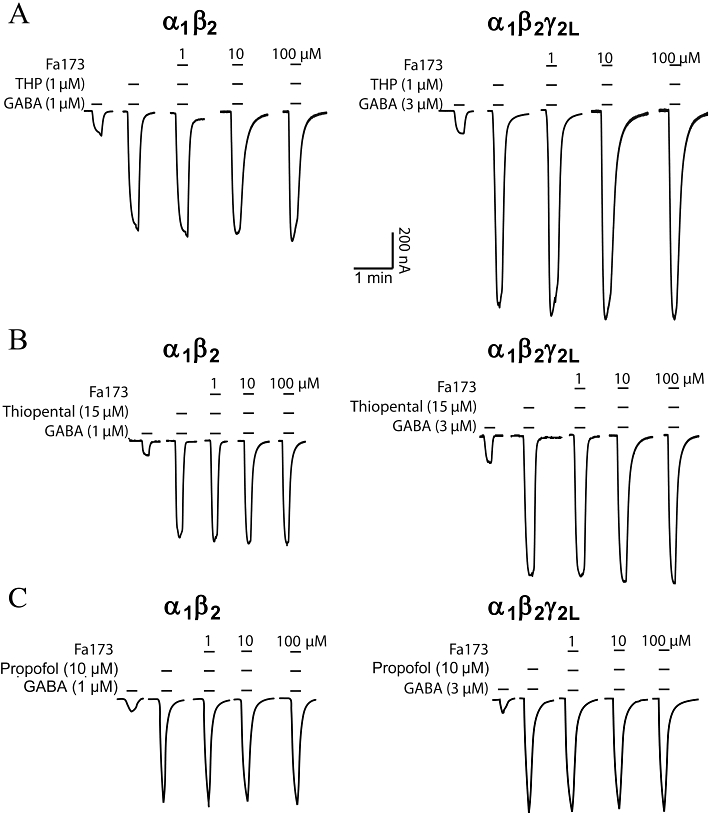
The flavan Fa173 failed to antagonize the potentiating effects induced by the neurosteroid THP and the barbiturate thiopental at recombinant α1β2 and α1β2γ2L GABAA expressed in Xenopus oocytes. (A) THP (1 µM) induced a potentiation of GABA-elicited currents, which could not be blocked by co-applying the flavan Fa73 at 1, 10 and 100 µM (n = 4). (B) The potentiation induced by thiopental (15 µM) was not affected by the co-application of the agent Fa173 (1–100 µM), at both receptor subtypes (n = 4). (C) Similarly, propofol (10 µM) induced a potentiation of GABA-elicited currents, that could not be blocked by co-applying the flavan Fa73 at 1, 10 and 100 µM (n = 3).
Fa173 blocks the GABA-potentiating effects induced by large, but not low, concentrations of diazepam
It has been well documented that diazepam can enhance GABA-induced currents in a biphasic mode when acting on α1β2γ2L GABAA receptors (Walters et al., 2000), an observation that has been reproduced in our laboratories (Hall et al., 2005). We selected two concentrations of diazepam to study the high-affinity (100 nM) and low-affinity (100 µM) effects of this drug at α1β2γ2L receptors (Figure 8A,B). At a concentration of 100 nM, diazepam induced a twofold potentiation of the GABA response, and this enhancement was completely blocked by the co-application of flumazenil 10 µM (93% inhibition), but not by Fa173 100 µM (2% inhibition, n = 3) (Figure 8A). However, when diazepam was applied at a high concentration (100 µM), flumazenil produced a mild neutralizing effect (about 10%), while the flavan Fa173 (100 µM) almost completely abolished the potentiation (87% inhibition, n = 3) (Figure 8B).
Figure 8.
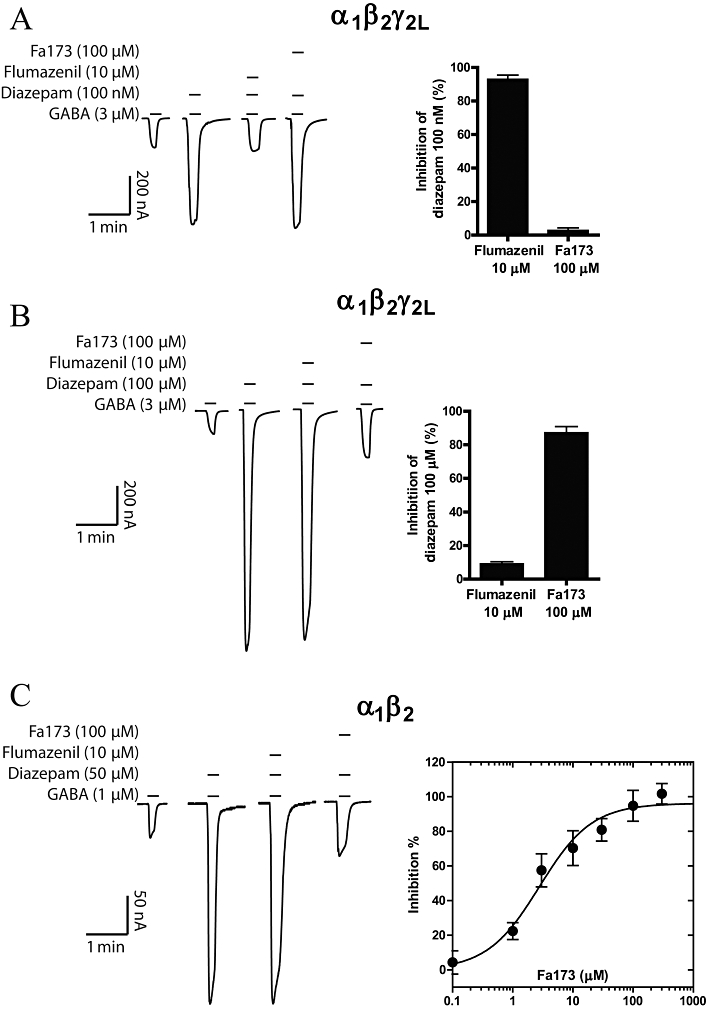
The flavan 173 selectively antagonizes the current enhancement induced by diazepam acting on its low-affinity site. (A) Representative current traces showing that Fa173 does not antagonize the potentiating effects of a low concentration of diazepam acting on α1β2γ2L receptors, while this effect is completely blocked by flumazenil (left panel). The quantification of the inhibitory effect of both drugs is shown on the right panel (n = 3). (B) Conversely, the response elicited by diazepam at a high concentration is blocked up to 87% by the flavan Fa173, while the co-application of flumazenil only inhibited about 10% of this response (n = 3). (C) At α1β2 receptors, diazepam induces a potentiation of GABA-elicited currents that can be almost completely blocked by the co-application of Fa173, but not flumazenil (left panel) (n = 4). The panel on the right shows the concentration-response curve for this effect (IC50 = 2.7 ± 0.8 µM, maximal inhibition = 94 ± 5%).
Conversely, at GABAA receptors composed of α1β2 subunits, diazepam potentiates GABA-induced currents in a monophasic manner, consistent with a single ‘low-affinity’ site. Diazepam (50 µM) induced a fivefold increase in GABA-elicited currents at this subunit combination, and this effect was unaffected by flumazenil (10 µM). However, when this dose of diazepam was co-applied with increasing concentrations of Fa173, the potentiation was completely abolished. Fa173 antagonized diazepam with an IC50 of 2.7 ± 0.8 µM and maximal inhibition of 94 ± 5% (n = 4) (Figure 8C).
Discussion
GABAA receptors expressing β2-N265 subunit
Etomidate and loreclezole present enhanced modulatory action at GABAA receptors that contain a β2/3 subunit, and their activity is comparatively weaker at β1 (Wafford et al., 1994; Hill-Venning et al., 1997). Later studies found that this selectivity was conferred by a single asparagine residue located at position 265 on the second transmembrane domain of the β2 subunit (and equivalent position at β3). When this asparagine is mutated to a serine (homologous amino acid in the β1 subunit), the ability of etomidate and loreclezole to potentiate GABA currents is diminished (Wafford et al., 1994; Wingrove et al., 1994; Belelli et al., 1997), and, accordingly, knock-in mice carrying either β3N265M or β2N265S present impaired sensitivity to the in vivo actions of these drugs (Jurd et al., 2003; Reynolds et al., 2003; Rudolph and Antkowiak, 2004; Groves et al., 2006). Notably, mutations at this point do not interfere with the potentiation induced by the neurosteroid alphaxalone and the barbiturate pentobarbitone (Belelli et al., 1999; Siegwart et al., 2003). In this study, the β2N265S mutant was co-expressed with α1 and γ2L subunits. As expected, etomidate and loreclezole were less capable of enhancing currents at this mutant receptor, but more interestingly, the modulatory action of Fa131 was also affected by this mutation, suggesting that these agents share a common binding site domain or signal transduction mechanism. Some studies utilizing computational modelling have suggested that this residue could contribute to the binding pocket for etomidate (Campagna-Slater and Weaver, 2007). However, more recent studies have suggested that N265 is not involved in the binding of etomidate (Li et al., 2006). As there is no high resolution crystal structure available for the GABAA receptor complex, the exact role of N265 remains unclear, dampening further speculations on our hypothesis.
GABAA receptors expressing α1-M236 subunit
In 2006, Li and collaborators, utilizing a radiolabelled photoreactive etomidate analogue, identified M236 at α-TM1 and M286 at β-TM3, to be directly involved in the binding of this anaesthetic (Li et al., 2006). In later work, Stewart et al. (2008) conducted a tryptophan mutation on M236 and characterized the properties of α1M236Wβ2γ2L receptors, showing that these channels present increased sensitivity to GABA transduction, and reduced etomidate modulation. Our α1M236Wβ2γ2L GABAA mutant receptors presented very similar characteristics to those described by Stewart et al., including augmented GABA gating, mild spontaneous activity and reduced potentiation by etomidate. Importantly, we found that this mutant was also less sensitive to allosteric modulation by loreclezole, and the flavan-3-ol Fa131, further reinforcing the idea that these three modulators share their binding pocket or activation domain. Interestingly, the mutation M236A did not affect the modulatory properties of etomidate, loreclezole or Fa131. Methionine, the original amino acid, tryptophan and alanine, the chosen mutations, all share the characteristics of non-polar hydrophobic amino acids; however, they differ largely in their molecular size. Thus, it is tempting to speculate that tryptophan impairs drug activity by sterically impeding the accommodation of large aromatic rings, or alternatively by offering nearby residues an intramolecular aromatic interaction, thus weakening the binding of a drug with similar needs. In this line, Stewart et al. (2008) proposed that a α1-M236W mutation mimicked the effects of etomidate on wild-type GABAA receptors. Conversely, alanine has a much smaller side chain that would allow the binding process to remain unaltered.
Fa173 is an antagonist of positive modulators such as Fa131, etomidate and loreclezole
Despite the worldwide use of GABAA receptor positive modulators in human therapy, the development of site-specific antagonists, best defined as neutral modulators, has been scarce. This may be due to the large number of sites for allosteric regulation present in these channels (Johnston, 2005). For example, positive or negative modulation by benzodiazepine ligands at the high-affinity site can be blocked by the antagonist flumazenil. Similarly, bemegride and 3α,5α-17-phenylandrost-16-en-3-ol have been proposed to be antagonists of the barbiturate and neurosteroid sites, respectively, but these drugs seem to present intrinsic limitations (Schechter, 1984; Mennerick et al., 2004). In our study, the flavan derivative Fa173 showed characteristics of a specific flavan-site modulator with extremely low efficacy to potentiate GABA-induced currents. Importantly, the main structural requirement for this change in intrinsic activity seems to be a cis conformation at C2 and C3. At recombinant α1β2 and α1β2γ2L receptors, Fa173 antagonized the potentiation induced by the positive modulator Fa131. Importantly, Fa173 also antagonized the enhancing effects of etomidate and loreclezole at α1β2 and α1β2γ2L receptors, suggesting that these drugs bind to a single binding site. However, it failed to neutralize the potentiating action of the neurosteroid THP, the barbiturate thiopental and the anaesthetic propofol.
As Fa173 had little direct effect on GABA-elicited currents, it is unlikely that this compound acts via binding to the GABA site. Rather, the antagonistic properties of Fa173 are highly selective, and may occur through competition for the etomidate/flavan site; however, further experimentation is needed to clarify the specific mechanism. Despite these reservations, this is, to our knowledge, the first report of a specific neutral modulator for the etomidate/loreclezole site and Fa173 represents a lead compound in the development of novel antagonists.
Diazepam binds to the ‘etomidate’ site with µM affinity
Both benzodiazepines and β-carbolines have been shown to possess two distinct components when interacting with GABAA receptors. The first component, via the classical benzodiazepine site, possesses high-affinity (nM), is flumazenil-sensitive and requires the presence of α1,2,3,5 and γ subunits. The second site presents low ligand affinity (µM), is insensitive to blockade by flumazenil and is not dependent on the presence of a γ subunit (Malherbe et al., 1990). It has been hypothesized that this second binding component could respond to an interaction with the etomidate/loreclezole site, as it could be eliminated by mutations at N265 in β2-TM2 (Stevenson et al., 1995; Walters et al., 2000). Our results corroborate this hypothesis; the flavan Fa173 blocked the effects of etomidate, loreclezole and high concentrations of diazepam at α1β2 and α1β2γ2L receptors. Importantly, we demonstrated that the two binding sites to which diazepam interacts with can be selectively blocked by the addition of flumazenil (high-affinity site) and Fa173 (low-affinity site).
Implications for anaesthetic action
Several mutational studies at M286 on β-TM3 led to the proposal that propofol may bind in the M3 domain near β2M286 (Krasowski et al., 1998; Siegwart et al., 2003). However, the finding that propofol only partially inhibits the affinity labelling of both α1M236 and β2M286 by [3H]-azietomidate suggests that the effect of propofol on the reaction of [3H]-azietomidate with these residues is allosteric rather than direct (Li et al., 2010). Importantly, the finding that Fa173 blocks potentiation by etomidate but not propofol supports the notion that propofol does not have a direct interaction with the etomidate binding site α1β2γ2L in GABAA receptors. Recently, the crystal structure of the bacterial LGIC with propofol bound was published, showing the location to be an inter-subunit cavity between the TM3 and TM4 domains (Nury et al., 2011). However, it is not yet known whether propofol binds in a similar location at GABAA receptors.
We previously observed that while the intrinsic activity of the flavan Fa131 on GABAA receptors resembled general anaesthetics, its in vivo profile was quite distinct. Unlike drugs such as etomidate, loreclezole and diazepam, Fa131 failed to induce strong sedative and hypnotic effects in mice. Rather, it exerted a robust anxiolytic action, as measured by the elevated plus maze and the light/dark paradigm. This discrepancy can be explained by the higher efficacy of Fa131 to activate GABAA receptors containing an α2 subunit (Fernandez et al., 2008), as this GABAA receptor subtype is believed to mediate the anxiolytic activity of benzodiazepines and barbiturates (Möhler et al., 2002; Dixon et al., 2008). In contrast, etomidate and loreclezole present limited α-subunit selectivity and their ability to induce sedation, anaesthesia and seizure protection is markedly subjugated by the activation of all β2/3-containing GABAA receptors, which represent more than 90% of all receptors expressed in the mammalian brain (Rudolph and Antkowiak, 2004; Groves et al., 2006). Benzodiazepines, such as diazepam, are much used as therapy for anxiety, but this group of substances has also proved useful as anticonvulsants, hypnotics and muscle relaxants. However, this spectrum of pharmacological activities does not all occur in the same dose range, and extensive studies have suggested that the incremental CNS effects of benzodiazepines may be the consequence of gradual nM receptor occupancy (Gardner, 1988; Ito et al., 1993; 1997). The identification of a second µM potentiation component, present in any αXβ2/3 subunit combination, thus less specific, indicates the possibility that the deep CNS-depressant actions of benzodiazepines could be the result of their effect, at µM concentrations, on GABAA receptor channels (Walters et al., 2000). Whether flumazenil does (Hoffman and Warren, 1993), or does not (Little and Bichard, 1984), antagonize the anaesthetic effects of benzodiazepines, might reveal whether a double nM/µM potentiation is an essential requirement. However, despite these speculations, the physiological and pharmacological relevance of the low-affinity benzodiazepine site is currently unknown, and, consequently, the development of a site-specific antagonist such as Fa173 may assist in addressing this question.
Conclusions
In summary, our studies have demonstrated that Fa173 is a selective antagonist that can be used for allosteric modulation of GABAA receptors. Using a combination of mutational studies and this novel ligand, we showed that flavan-3-ol derivatives are potential ligands for etomidate/loreclezole-related binding sites at GABAA receptors. Furthermore, the low-affinity potentiation induced by benzodiazepines, perhaps related to their high-dose anaesthetic-like effects, can also be explained by a second binding component to this same site.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a grant from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia. NK acknowledges funding from The University of Malakand, Pakistan (Faculty Development Programme Scholarship) and a John Lamberton Scholarship The authors are grateful to Dr Paul Whiting for providing GABAA receptor subunit DNAs.
Glossary
- DMSO
dimethyl sulphoxide
- Fa131
2S,3R-trans 3-acetoxy-4′-methoxyflavan
- Fa173
2S,3S-cis 3-acetoxy-3′,4′-dimethoxyflavan
- LGIC
ligand-gated ion channel
- THP
5α-pregnan-3α-ol-20-one
- TM
transmembrane
Conflict of interest
The authors state no conflict of interest.
References
- Akk G, Li P, Bracamontes J, Reichert DE, Covey DF, Steinbach JH. Mutations of the GABAA receptor α1 subunit M1 domain reveal unexpected complexity for modulation by neuroactive steroids. Mol Pharmacol. 2008;74:614–627. doi: 10.1124/mol.108.048520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander SPH, Mathie A, Peters JA. Guide to receptors and channels (GRAC), 5th edition. Br J Pharmacol. 2011;164(Suppl. 1):S1–S324. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01649_1.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belelli D, Lambert JJ. Neurosteroids: endogenous regulators of the GABAA receptor. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005;6:565–575. doi: 10.1038/nrn1703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belelli D, Lambert JJ, Peters JA, Wafford K, Whiting PJ. The interaction of the general anesthetic etomidate with the γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor is influenced by a single amino acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:11031–11036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.20.11031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belelli D, Pistis M, Peters JA, Lambert JJ. The interaction of general anaesthetics and neurosteroids with GABAA and glycine receptors. Neurochem Int. 1999;34:447–452. doi: 10.1016/s0197-0186(99)00037-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campagna-Slater V, Weaver DF. Anaesthetic binding sites for etomidate and propofol on a GABAA receptor model. Neurosci Lett. 2007;418:28–33. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2007.02.091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang CS, Olcese R, Olsen RW. A single M1 residue in the β2 subunit alters channel gating of GABAA receptor in anesthetic modulation and direct activation. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:42821–44288. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M306978200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai R, Ruesch D, Forman SA. γ-Amino butyric acid type A receptor mutations at β2N265 alter etomidate efficacy while preserving basal and agonist-dependent activity. Anesthesiology. 2009;111:774–784. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181b55fae. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon CI, Rosahl TW, Stephens DN. Targeted deletion of the GABRA2 gene encoding α2-subunits of GABAA receptors facilitates performance of a conditioned emotional response, and abolishes anxiolytic effects of benzodiazepines and barbiturates. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2008;90:1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2008.01.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drafts BC, Fisher JL. Identification of structures within GABAA receptor alpha subunits that regulate the agonist action of pentobarbital. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006;318:1094–1101. doi: 10.1124/jpet.106.104844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez SP, Mewett KN, Hanrahan JR, Chebib M, Johnston GA. Flavan-3-ol derivatives are positive modulators of GABAA receptors with higher efficacy for the alpha(2) subtype and anxiolytic action in mice. Neuropharmacology. 2008;55:900–907. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.06.069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner CR. Functional in vivo correlates of the benzodiazepine agonist-inverse agonist continuum. Prog Neurobiol. 1988;31:425–476. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(88)90011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groves JO, Guscott MR, Hallett DJ, Rosahl TW, Pike A, Davies A, et al. The role of GABA β2 subunit-containing receptors in mediating the anticonvulsant and sedative effects of loreclezole. Eur J Neurosci. 2006;24:167–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.04890.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall BJ, Chebib M, Hanrahan JR, Johnston GAR. 6-Methylflavanone, a more efficacious positive allosteric modulator of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) action at human recombinant α2β2γ2L than at α1β2γ2L and α1β2 GABAA receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Eur J Pharmacol. 2005;512:97–104. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.02.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill-Venning C, Belelli D, Peters JA, Lambert JJ. Subunit-dependent interaction of the general anaesthetic etomidate with the gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1997;120:749–756. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0700927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman EJ, Warren EW. Flumazenil: a benzodiazepine antagonist. Clin Pharm. 1993;12:641–656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosie AM, Wilkins ME, da Silva HM, Smart TG. Endogenous neurosteroids regulate GABAA receptors through two discrete transmembrane sites. Nature. 2006;444:486–489. doi: 10.1038/nature05324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K, Yamada Y, Nakamura K, Sawada Y, Iga T. Classification of benzodiazepine hypnotics in humans based on receptor occupancy theory. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1993;21:31–41. doi: 10.1007/BF01061774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K, Asakura A, Yamada Y, Nakamura K, Sawada Y, Iga T. Prediction of the therapeutic dose for benzodiazepine anxiolytics based on receptor occupancy theory. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 1997;18:293–303. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1099-081x(199705)18:4<293::aid-bdd24>3.0.co;2-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston GAR. GABAA receptor channel pharmacology. Curr Pharm Des. 2005;11:1867–1885. doi: 10.2174/1381612054021024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurd R, Arras M, Lambert S, Drexler B, Siegwart R, Crestani F, et al. General anesthetic actions in vivo strongly attenuated by a point mutation in the GABAA receptor beta3 subunit. FASEB J. 2003;17:250–252. doi: 10.1096/fj.02-0611fje. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasowski MD, Koltchine VV, Rick CE, Ye Q, Finn SE, Harrison NL. Propofol and other intravenous anesthetics have sites of action on the γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor distinct from that for isoflurane. Mol Pharmacol. 1998;53:530–538. doi: 10.1124/mol.53.3.530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li GD, Chiara DC, Sawyer GW, Husain SS, Olsen RW, Cohen JB. Identification of a GABAA receptor anesthetic binding site at subunit interfaces by photolabeling with an etomidate analog. J Neurosci. 2006;26:11599–11605. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3467-06.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li GD, Chiara DC, Cohen JB, Olsen RW. Numerous classes of general anesthetics inhibit etomidate binding to γ-aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA) receptors. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:8615–8620. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.074708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little HJ, Bichard AR. Differential effects of the benzodiazepine antagonist Ro 15-1788 after ‘general anaesthetic’ concentrations of benzodiazepines in mice. Br J Anaesth. 1984;56:1153–1160. doi: 10.1093/bja/56.10.1153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malherbe P, Draguhn A, Multhaup G, Beyreuther K, Möhler H. GABAA-receptor expressed from rat brain α- and β-subunit cDNAs displays potentiation by benzodiazepine receptor ligands. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1990;8:199–208. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(90)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKernan RM, Whiting PJ. Which GABAA-receptor subtypes really occur in the brain? Trends Neurosci. 1996;19:139–143. doi: 10.1016/s0166-2236(96)80023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mennerick S, He Y, Jiang X, Manion BD, Wang M, Shute A, et al. Selective antagonism of 5α-reduced neurosteroid effects at GABAA receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 2004;65:1191–1197. doi: 10.1124/mol.65.5.1191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mewett KN, Fernandez SP, Pasricha AP, Pong A, Devenish SO, Hibbs DE, et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of flavan-3-ol derivatives as positive modulators of GABAA receptors. Bioorg Med Chem. 2009;17:7156–7173. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2009.08.062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller PS, Smart TG. Binding, activation and modulation of Cys-loop receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2010;31:161–174. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2009.12.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhler H, Fritschy JM, Rudolph U. A new benzodiazepine pharmacology. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002;300:2–8. doi: 10.1124/jpet.300.1.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nury H, Van Renterghem C, Weng Y, Tran A, Baaden M, Dufresne V, et al. X-ray structures of general anaesthetics bound to a pentameric ligand-gated ion channel. Nature. 2011;469:428–431. doi: 10.1038/nature09647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds DS, Rosahl TW, Cirone J, O'Meara GF, Haythornthwaite A, Newman RJ, et al. Sedation and anesthesia mediated by distinct GABAA receptor isoforms. J Neurosci. 2003;23:8608–8617. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-24-08608.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph U, Antkowiak B. Molecular and neuronal substrates for general anaesthetics. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2004;5:709–720. doi: 10.1038/nrn1496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter MD. Specific antagonism of the behavioral effects of chlordiazepoxide and pentobarbital in the rat. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 1984;8:359–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegwart R, Krähenbühl K, Lambert S, Rudolph U. Mutational analysis of molecular requirements for the actions of general anaesthetics at the γ-aminobutyric acidA receptor subtype, α1β2γ2. BMC Pharmacol. 2003;3:13. doi: 10.1186/1471-2210-3-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J, Wakimoto H, Fujita N, Lalande M, Barnard EA. Analysis of the set of GABAA receptor genes in the human genome. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:41422–41435. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M401354200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson A, Wingrove PB, Whiting PJ, Wafford KA. β-carboline γ-aminobutyric acid A receptor inverse agonists modulate γ-aminobutyric acid via the loreclezole binding site as well as the benzodiazepine site. Mol Pharmacol. 1995;48:965–969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart D, Desai R, Cheng Q, Liu A, Forman SA. Tryptophan mutations at azi-etomidate photo-incorporation sites on α1 or β2 subunits enhance GABAA receptor gating and reduce etomidate modulation. Mol Pharmacol. 2008;74:1687–1695. doi: 10.1124/mol.108.050500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson SA, Whiting PJ, Wafford KA. Barbiturate interactions at the human GABAA receptor: dependence on receptor subunit combination. Br J Pharmacol. 1996;117:521–527. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb15221.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wafford KA, Bain CJ, Quirk K, McKernan RM, Wingrove PB, Whiting PJ, et al. A novel allosteric modulatory site on the GABAA receptor beta subunit. Neuron. 1994;12:775–782. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90330-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walters RJ, Hadley SH, Morris KD, Amin J. Benzodiazepines act on GABAA receptors via two distinct and separable mechanisms. Nat Neurosci. 2000;3:1274–1281. doi: 10.1038/81800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingrove PB, Wafford KA, Bain C, Whiting PJ. The modulatory action of loreclezole at the γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor is determined by a single amino acid in the β2 and β3 subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994;91:4569–4573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.10.4569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


