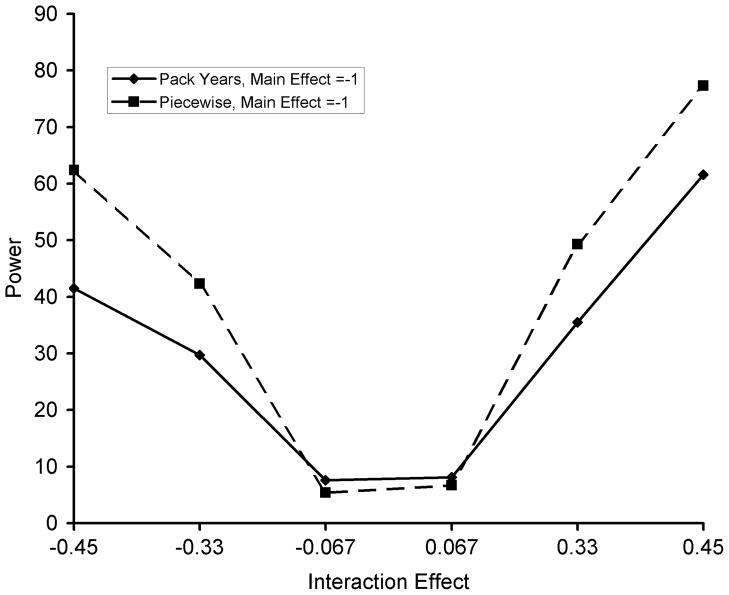
Figure 2.
Observed power to detect gene-by-smoking interactions for the pack-years versus piecewise linear approach to model smoking. Simulation study based on data from the Genetic Modifiers of Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Disease Study. Simulation parameters are as follows: minor allele frequency = 25%, genetic main effect = −1 unit from observed FEV1 percent predicted per copy of minor allele, gene-by-smoking effect varies as shown. For this power analysis, the threshold for detecting an effect was set at alpha <0.05 for the null hypothesis that the gene-by-smoking effect is equal to zero. For gene-by-smoking effects the piecewise linear model is more powerful. At low values of the gene-by-smoking interaction, the total pack-years approach appears more powerful due to upwardly biased estimates of the gene-by-smoking interaction (values shown in Table 2).