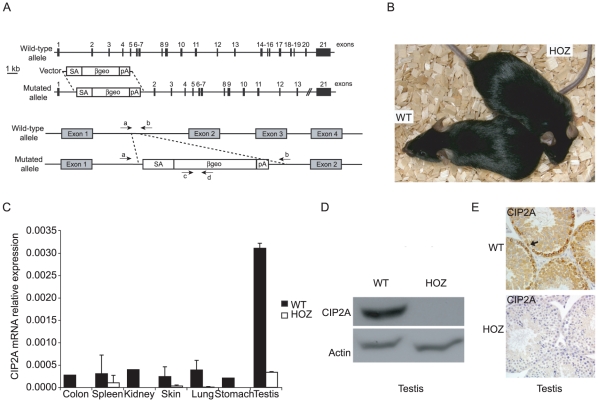
Figure 1. Characterization of hypomorphic CIP2AHOZ mice.
(A) Gene-trap strategy for inhibition of CIP2A expression. Murine CIP2A wild-type allele and the corresponding CIP2A locus with gene-trap vector insertion are presented in the upper panel (exon structure is represented with filled boxes, the gene-trap vector by clear boxes). The pGT0Lxf gene-trap vector contains a splice acceptor site (SA), β-galactosidase reporter gene (β-geo) and a SV40 polyadenylation site (pA) inserted in CIP2A locus intron 1. The lower panel indicates the position of the genotyping primers, a–b for the wild-type allele, c–d for the mutated allele. (B) CIP2AHOZ mice grow and develop normally. There were no differences in morphology between adult WT or CIP2AHOZ mice. (C) CIP2A mRNA expression in WT and CIP2AHOZ adult mouse organs. Real-time PCR analysis for CIP2A mRNA in CIP2A expressing organs. Mouse beta-actin was used for normalization. (D) CIP2A protein expression in WT and HOZ testis tissue. (E) CIP2A immunoreactivity in WT and HOZ testis was evaluated by immunohistochemistry. No CIP2A protein expression was detected in CIP2AHOZ tissues. Arrows indicate specific CIP2A staining in WT basal male germ cells.