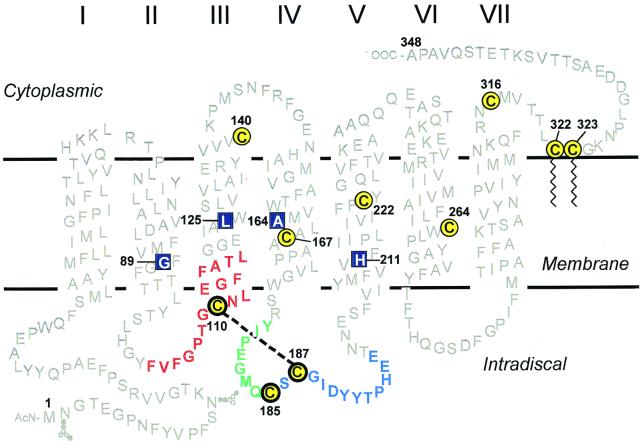
Figure 1.
A secondary structure model of rhodopsin showing the cytoplasmic, TM, and the ID domains. The 10 cysteines are shown in yellow with black circles; the three ID cysteines are highlighted by bolder circles. Amino acid sequences adjoining the three cysteines of interest (for identification of the disulfide bonds) are color coded for each cysteine: red for Cys-110, green for Cys-185, and blue for Cys-187. Native rhodopsin contains a disulfide bond between Cys-110 and Cys-187 (indicated by dashed line). The RP mutants studied here are located in the TM domain (shown in blue boxes): G89D (helix II), L125R (helix III), A164V (helix IV), and H211P (helix V).