Figure 3.
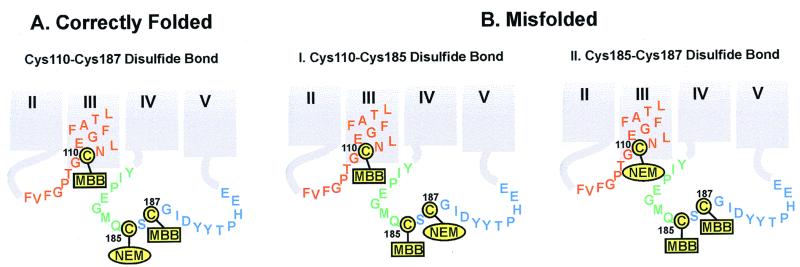
Derivatizations as expected for ID cysteines in correctly folded (A) and misfolded (B) rhodopsins. The disulfide linkage in correctly folded A rhodopsin is between Cys-110 and Cys-187, as identified by mass spectrometry (Fig. 4). Thus, steps 1 and 2 of the strategy in the identification of disulfide bonds (see above) produced rhodopsin NEM-derivatized at Cys-185, whereas Cys-110 and Cys-187 were derivatized with MBB. In misfolded rhodopsin B, the disulfide bond could either be between Cys-110 and Cys-185 (I) or between Cys-185 and Cys-187 (II). Experimentally, the disulfide bond was found between Cys-185 and Cys-187 (Fig. 4). Thus, Cys-110 was NEM-derivatized, whereas Cys-185 and Cys-187 were MBB-derivatized (II). The color code for the amino acid residues adjacent to each of the cysteines is the same as in Fig. 1. The derivatized products were then subjected to steps 3–5 (above), yielding the MBB-derivatized peptides that were analyzed by MALDI-TOF (Fig. 4).