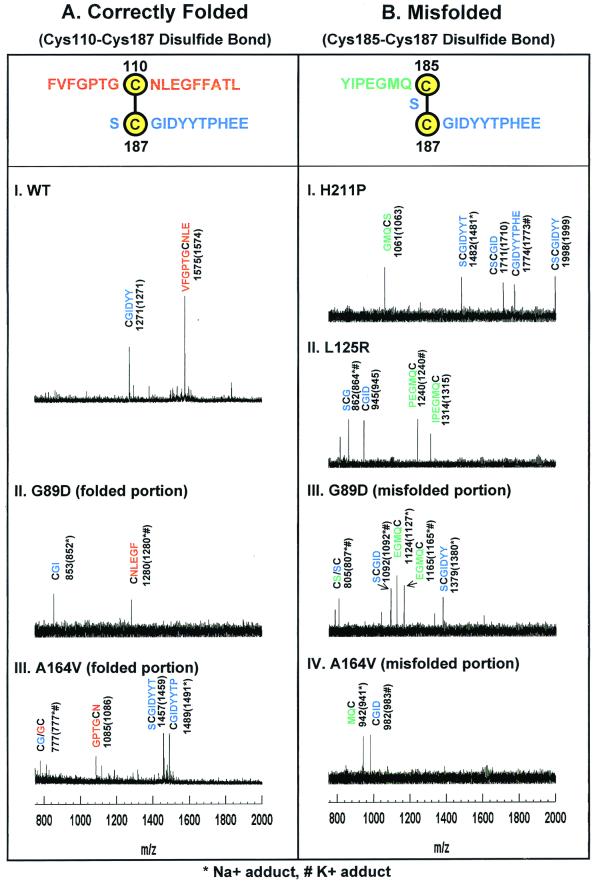
Figure 4.
MALDI-TOF Analysis of peptide fragments generated from the derivatized correctly folded (A) and misfolded (B) rhodopsins. The adjoining peptide sequences expected for the disulfide bonds are highlighted at the top in A and B. Rhodopsins were derivatized at cysteines as in the strategy outlined above. Because step 4 of the strategy selects only MBB-labeled peptides, all peptide assignments shown here include the mass for the MBB adducts of cysteines. The y axis shows intensity in arbitrary units. The x axis shows m/z in the range of 750–2,000. (A) Mass spectrometric results for WT rhodopsin and correctly folded portions of the A164V and G89D mutants. The observed signals in the mass spectra correspond to MBB-labeled Cys-110 peptides (red) and Cys-187 peptides (blue). (B) Mass spectrometric results for the misfolded portion of A164V and G89D (III and IV) and of completely misfolded H211P and L125R (I and II). Only peptides corresponding to a Cys-185–Cys-187 disulfide bond were observed. MBB-labeled Cys-185 containing peptides are shown in green, and MBB-labeled Cys-187 peptides are shown in blue.