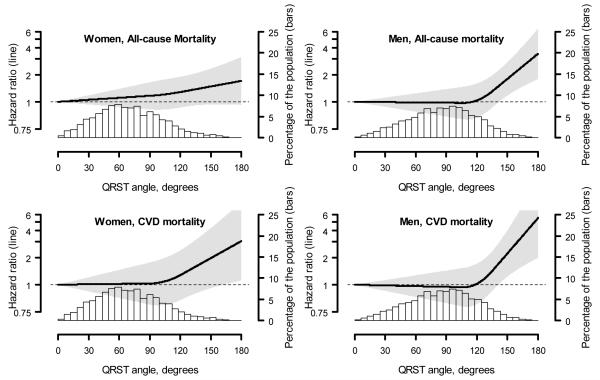
Figure 1.
Multivariable adjusted hazard ratios for all-cause (top panels) and cardiovascular mortality (bottom panels) associated with spatial QRS|T angle, modeled as a continuous variable using restricted quadratic splines. Spline knots were placed at the 75th and 95th percentiles of the spatial QRS/T angle distribution for women (90° and 121°, respectively) and men (107° and 136°, respect ively).
Multivariable adjustment includes age, race/ethnicity, sex, body mass index, physical inactivity, current smoking, systolic blood pressure, antihypertensive medication use, heart rate, diabetes, total and HDL-cholesterol, cholesterol lowering medication use, C-reactive protein ≥ 3 mg/L, reduced estimated glomerular filtration rate, albuminuria, and a history of stroke.