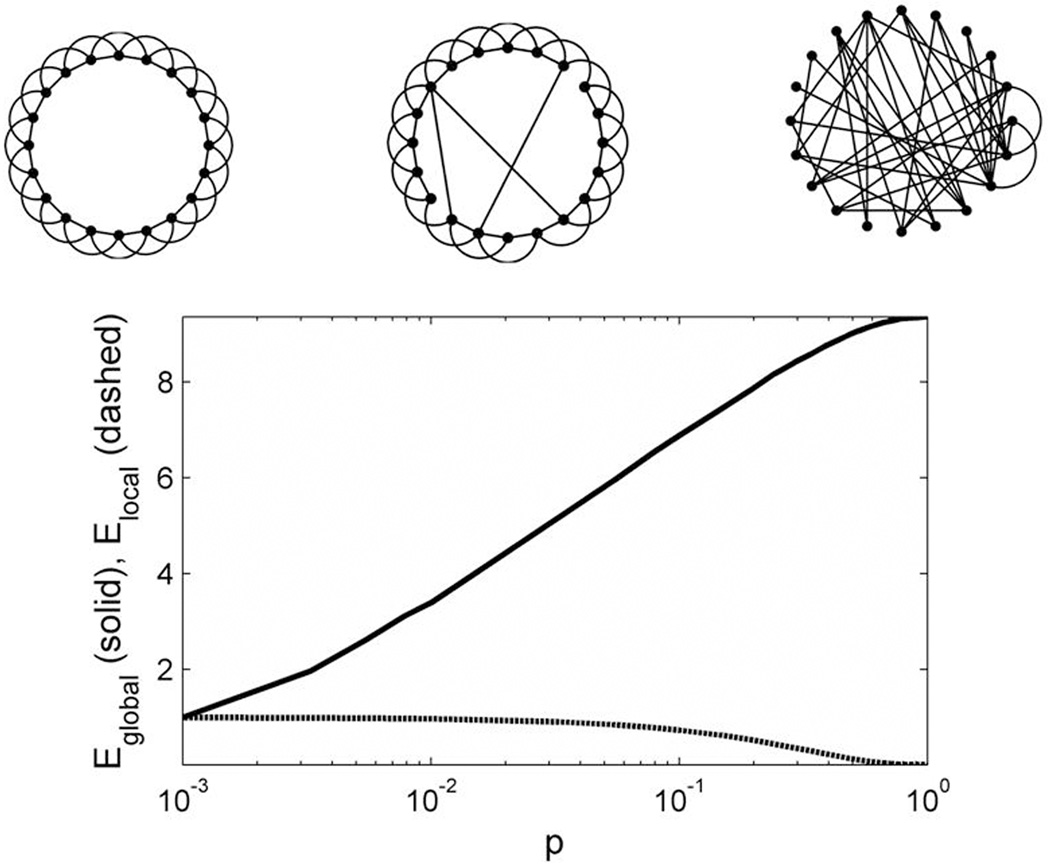
Figure 1. Network architectures and efficiency statistics.
(A) Different types of networks. Regular network in which nodes are connected only to their two nearest neighbors on either side (left). Small world network, in which a small number of local connections are replaced by long-distance connections at random locations (center). Random network, in which nodes are connected at random, with a resulting loss of local connectivity (right). (B) Global efficiency (Eglobal, solid line) and local efficiency (Elocal, dashed line) as a function of the probability of random connections.