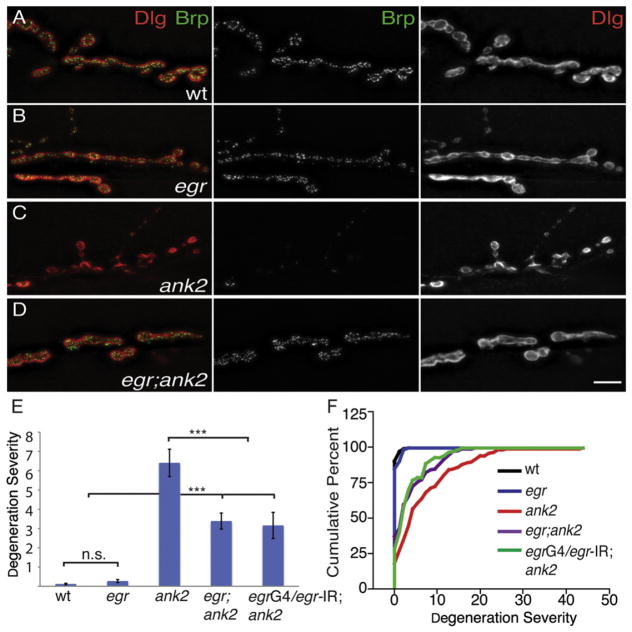
Figure 2. eiger Suppresses ank2-Dependent Degeneration at the NMJ.
(A–D) Representative images of third-instar muscle 6/7 NMJs stained with the presynaptic active zone marker Brp (green, middle panels) and the postsynaptic marker Dlg (red, right panels). (A) A wild-type NMJ showing presynaptic Brp (green, middle panel) in perfect apposition with postsynaptic Dlg (red, right panel). (B) eiger null mutations do not affect NMJ morphology or colocalization of Brp (green, middle panel) and Dlg (red, right panel) at muscle 6/7. (C) NMJ of a homozygous ank2 animal showing organized postsynaptic Dlg (red, right panel) with very little opposing presynaptic Brp staining, indicating that the presynaptic nerve terminal has been eliminated. (D) Animals that are homozygous for both eiger and ank2 have a remarkably improved NMJ despite the presence of the ank2 mutation. Presynaptic Brp (green, middle panel) now colocalizes with postsynaptic Dlg (red, right panel) staining. Scale bar, 10 μm.
(E and F) Quantification of degeneration severity (E) is measured as the average number of boutons retracted per individual NMJ, and cumulative percentage of degeneration severity (F) is plotted as cumulative frequency histogram for each genotype. wt = w1118 (n = 129 NMJs); egr = egrΔ25/egrΔ25 (n = 75 NMJs); ank2 = ank22001/ank22001 (n = 141 NMJs); egr; ank2 = egrΔ25/egrΔ25; ank22001/ank22001 (n = 129 NMJs); egrG4/egr-IR; ank = egr-GAL4/pUAS-egr-RNAi; ank/ank (n = 90). Error bars represent SEM. p values were determined using one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey-Kramer: ***p < 0.001. Statistical differences remain when comparisons are made using Student’s t test. n.s., not significant.