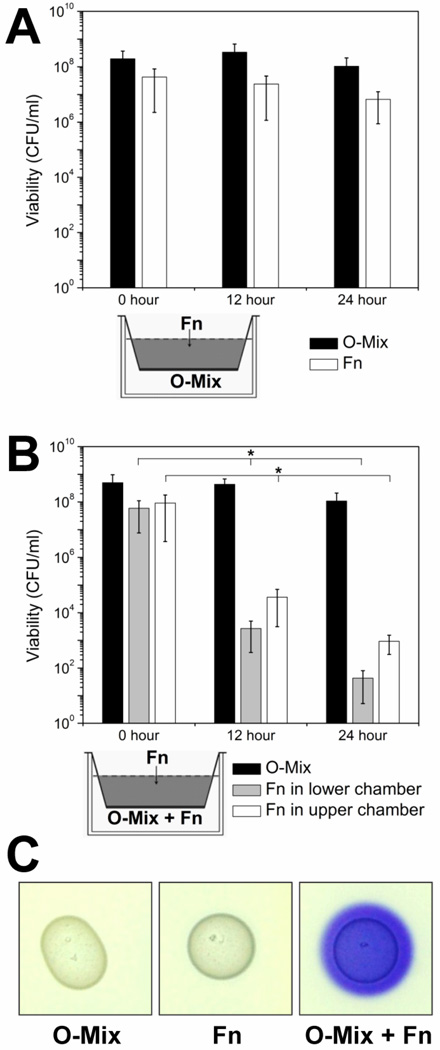
Figure 1. Contact-dependent killing of F. nucleatum by the O-mix.
(A) Two-chamber assay in which F. nucleatum (Fn) was inoculated into the upper chamber and physically separated from the O-mix in the lower chamber by a 0.4 µm pore size membrane (as shown in the small diagram). Viability of F. nucleatum (open bars) and O-mix (solid bars) was tracked every 12 hours by determining viable counts.
(B) Two-chamber assay in which F. nucleatum was added to the upper chamber, while O-mix, together with F. nucleatum (at a 10:1 ratio) was inoculated into the lower chamber. Viability was monitored for O-mix and F. nucleatum in both chambers (black solid bars represent total viable counts of O-mix, grey bars and open bars represent viable count of F. nucleatum in the lower and upper chamber, respectively). Two independent experiments were performed in three replicates each, and average values ± SD are shown. The asterisk indicates that the values of 12 and 24 hour were significantly lower than the one for 0 hour (Student’s t-test p value < 0.05).
(C) F. nucleatum triggers the release of H2O2 in O-mix cells. O-mix and wild type F. nucleatum were spotted individually or mixed together on BHI agar plates containing leuco crystal violet and Horseradish peroxidase, purple color development was monitored after overnight incubation. Three replicates were performed and a representative result is shown.