Figure 5.
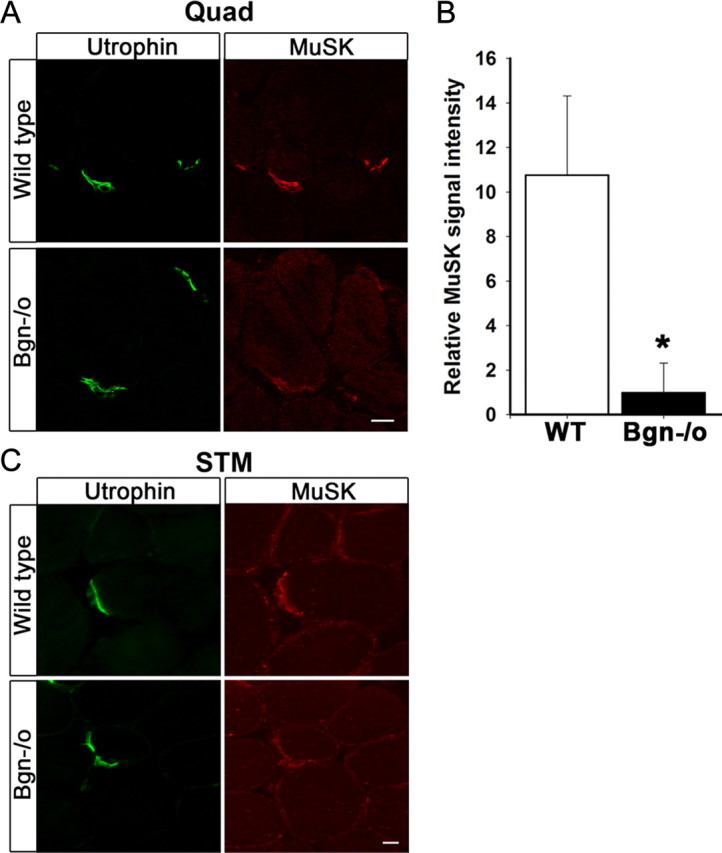
MuSK expression is decreased at synapses in biglycan null mice. A, Quadriceps femoris sections from 5-week-old wild-type and biglycan null animals were immunolabeled with a mouse anti-utrophin (green) and a rabbit anti-MuSK (affinity purified 29–31, see Materials and Methods, Antibodies; red). Utrophin is expressed at similar levels at synapses in wild-type and biglycan null muscle. However, a decrease in the intensity of MuSK staining at biglycan null neuromuscular junctions is observed. Scale bar, 10 μm. B, The mean pixel signal intensity of MuSK normalized to the mean pixel signal intensity of utrophin at the neuromuscular junctions of wild-type, 10.78 ± 3.54, and biglycan null muscle, 1.00 ± 1.32 (at least 3 synapses per condition) was determined as described in Materials and Methods. The signal intensity of MuSK was significantly higher at wild-type versus biglycan null junctions (Student's unpaired t test, *p < 0.02). C, Sternomastoid sections from 5-week-old wild-type and biglycan null mice were immunolabeled as in A. Utrophin is expressed at similar levels at the synapses in wild-type and biglycan null sternomasoid while synaptic MuSK is decreased in the biglycan null sternomastoid muscle. Scale bar, 10 μm.
