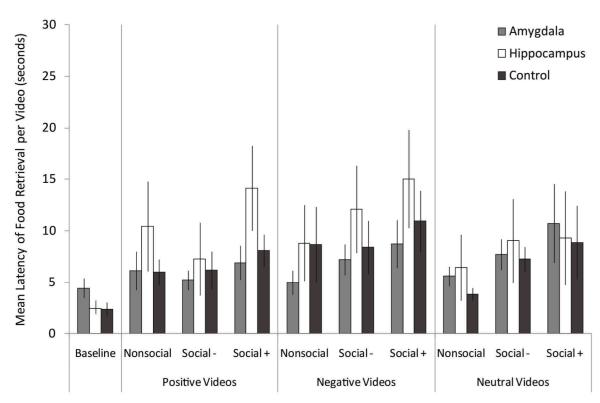
Figure 1.
Food Retrieval Latency
Data columns depict the average time to retrieve food per video type; error bars represent standard errors of the means. Note that the figure uses raw data for the ease of interpretation, although log transformed data were analyzed. Amygdala: amygdala-lesioned animals; Hippocampus: hippocampus-lesioned animals; Control: control animals. Baseline: baseline trials with screen saver video. Affective Content Categories—Positive: videos with positive affective content; Negative: videos with negative affective content. Neutral: videos with neutral affective content. Social Content Categories—Nonsocial: Nonsocial videos. Social−: Social non-engaging videos. Social+: Social engaging videos.
There were no significant, or marginally significant, lesion group differences in the latency to retrieve food within each specific stimulus type positive nonsocial videos, negative social engaging videos, etc.).