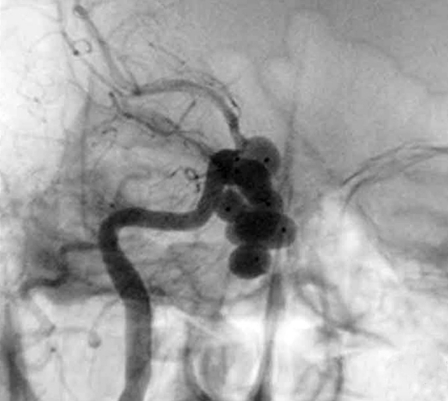
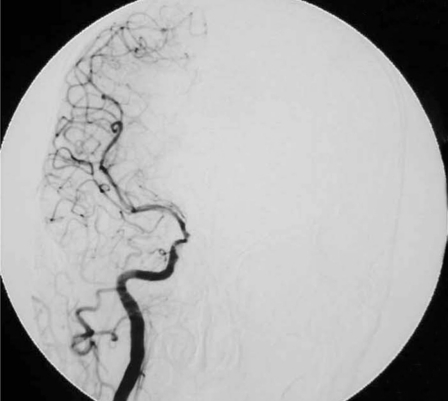
Figure 2.
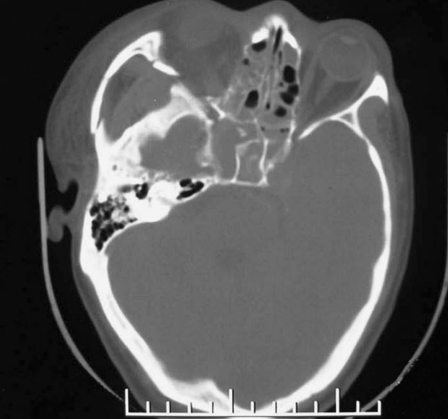
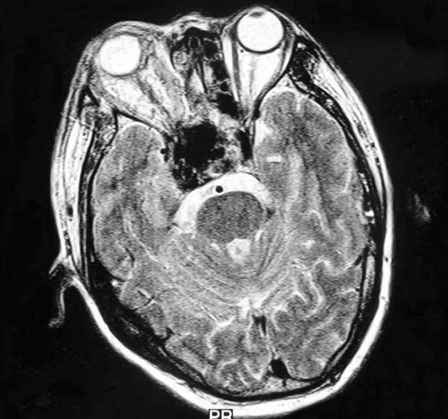
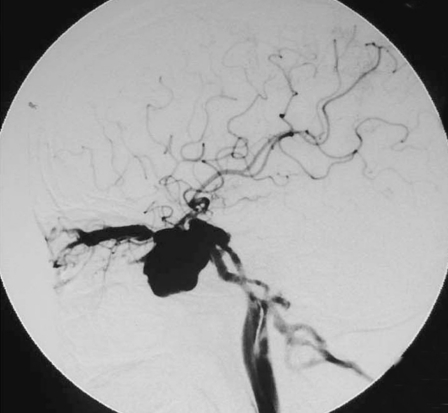
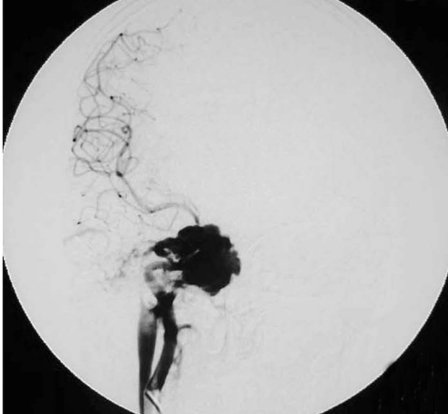
Case 6, a 44-year-old man with right side chemosis, visual field defect, intracranal bruit had suffered trauma caused by a falling from high speed motorcycle, and had episode of massive epistaxis three days after the accident. A) Early CT scans revealed fracture at the right zygomatic arch, sphenoid and ethmoid sinus, soft tissue density in the sphenoid sinus. B) Subsequent T2-weighted axial MRI scan demonstrated a large signal-void aneurysm in the sphenoid sinus and a dilated right side cavernous sinus. C?An irregular pseudoaneurysm projecting anteroinferiorly into the sphenoid sinus with concomitant traumatic carotid cavernous fistula draining via the superior ophthalmic vein and inferior petrosal sinus was found on lateral view of right interal carotid angiogram. D) Anteroposterior view also demonstrated that there was minimal flow in the supraclinoid portion of the right ICA,and the right A1 was dysplastic. E) Anteroposterior unsubtracted and F) subtracted film showed the fistula and the pseudoaneurysm were occluded by the eight detachable latex balloons with preservation of the parent artery.