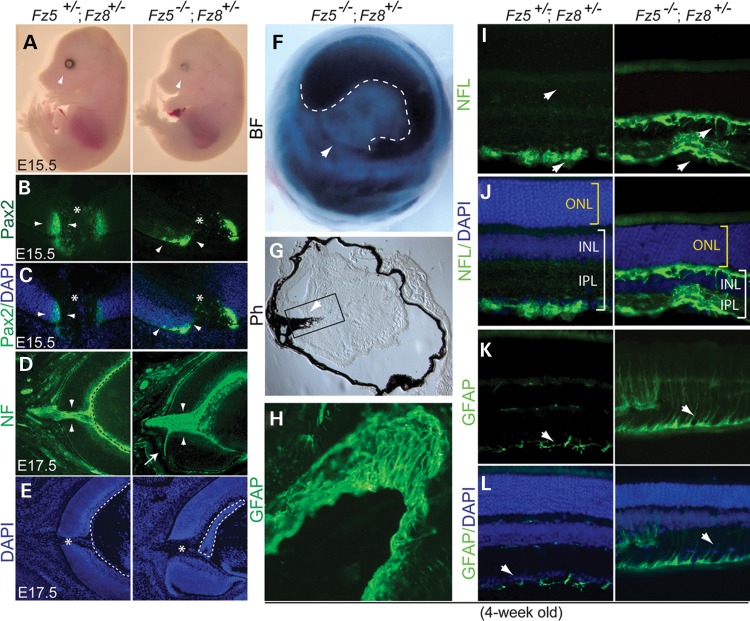
Figure 2.
Severe retinal coloboma, microphthalmia, retinal gliosis and axon sprouting in the Fz5−/−;Fz8+/− mutant retina. (A) Lacking ventral retinal tissue, severe retinal coloboma and microphthalmia at E15.5 in the Fz5−/−;Fz8+/− compound mutant retina (arrowheads). (B) Staining of Pax2 at optic fissure is more restricted in the WT (arrowheads, left panel) than in the mutant (arrowheads, right panel). Asterisks indicate the optic discs. (C) Merged images of Pax2 staining with DAPI indicate the retinal structure at optic disc. (D and E) Widened optic fissure with massive RGC axons routing out the mutant retina at E17.5. Misrouting of axons often happens (white arrow, right panel) with a consistently observed thickened retinal neural fiber layer and malformation of retinal fetal vasculature (dashed lines enclosure). (E) DAPI staining of the same sections in (D) showing the retinal structure of optic disc area (asterisk) at E17.5. Dashed lines indicate the embryonic vasculature tissues. (F) A brightfield (BF) picture of 4-week-old mutant eyeball showing the server ventral retinal coloboma (arrowhead). The pupil-iris boundary is demarcated by dashed lines. (G) Phase contrast image of a 4-week-old retinal section showing severely deformed mutant retina and intraocular pigmented PFV (arrowhead). (H) Boxed area in G showing overwhelming GFAP-stained astroglia lining the surface of unclosed optic fissure. (I) NFL-stained axon sprouting in the 4-week-old compound mutant retina in both GCL and OPL (arrows). (J) Images from (I) merged with DAPI showing inner retina thickness (white brackets, INL and IPL) is significantly reduced in the mutant compared with the WT. Mutant ONL thickness is similar to the WT at this stage (yellow brackets). (K) Abnormal glial activation in the mutant retina. GFAP-labeled astrocytes sparsely distribute below the GCL in the WT retina, while they spread along the neural fiber layer in the mutant retina (arrows) and go up to through the mutant retina. (L) DAPI-stained retinal nuclear layers merged with GFAP staining shown in (K).