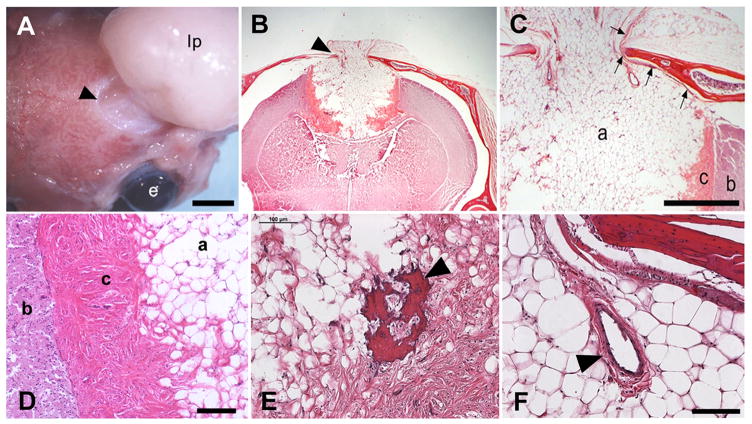
Figure 4.
Gross and histological analysis of affected 3H1 tuft mice. (A) Large, extracranial lipoma (lp) connected to the meninges through the exit foramen (arrowhead). Bar = 3 mm; e, eye. (B) Coronal histological section showing a large encapsulated cortical lipoma exiting the skull in the midline (arrowhead). (C) Higher magnification of (B) revealing the adipose (a) extending through the skull and was bordered by a distinct fibrous capsule (c) separating the mass from the brain parenchyma (b). Arrows point to the dura that lined and connected with the mass as it exited. Bar = 1.0 mm. (D) Higher magnification showing morphologies and boundaries separating the brain parenchyma (b), fibrous capsule (c) and adipose (a). Bar = 100 microns. (E) Bone spicule within the fibrous capsule (arrowhead). Bar = 100 microns (F) Blood vessel within the lipomatous mass (arrowhead). Bar = 100 microns