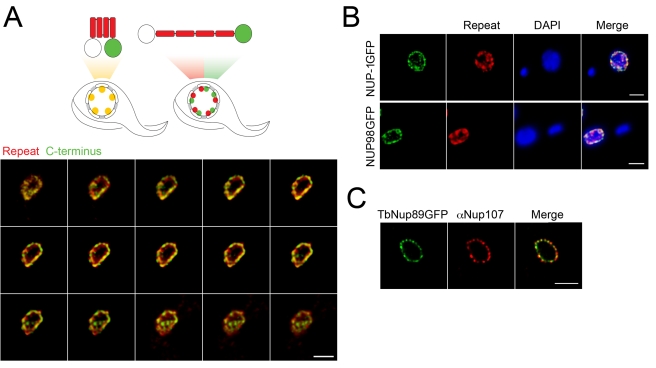
Figure 3. NUP-1 is arranged in an extended conformation.
(A) Top: Schematic showing NUP-1 in either a compact (left) or an extended (right) conformation. Repeats are shown in red, and the GFP-tagged C-terminal domain is in green. The untagged N-terminus is white. Predicted staining patterns for each conformer are shown below the schematics. Lower: Cells expressing NUP-1-GFP were probed with anti-GFP (green) and anti-NUP-1 repeat region antibody (red) and imaged by confocal microscopy. A montage of 15 confocal z-stack slices through the nucleus of a single trypanosome is shown. There is clear discrimination between the red and green channels, consistent with an extended conformation. (B) Top: Cells expressing NUP-1-GFP were probed with an anti-GFP (green) antibody and a secondary antibody that was immunoabsorbed to eliminate cross-species reactivity and anti-NUP-1 repeat region antibody (red) and imaged by confocal microscopy. Shown is a central slice across the z-axis. DAPI was used to visualise DNA. Bar: 2 µm for all panels. In independent stains using either the anti-GFP or repeat region antibodies alone, it was clear that there was no cross-reactivity (unpublished data). Lower: Cells expressing TbNup98-GFP were probed with anti-GFP (green) and anti-NUP-1 repeat region antibody (red) and imaged by confocal microscopy. Shown is the central slice along the z-axis, also demonstrating clear separation of the nuclear pore complex from the NUP-1 repeat staining. (C) Cells expressing TbNup89-GFP were probed with anti-GFP (green) and an anti-FG repeat antibody (red) to visualize the NPCs and imaged by confocal microscopy. There is clear high correspondence between the red and green stains, consistent with previous data [36].