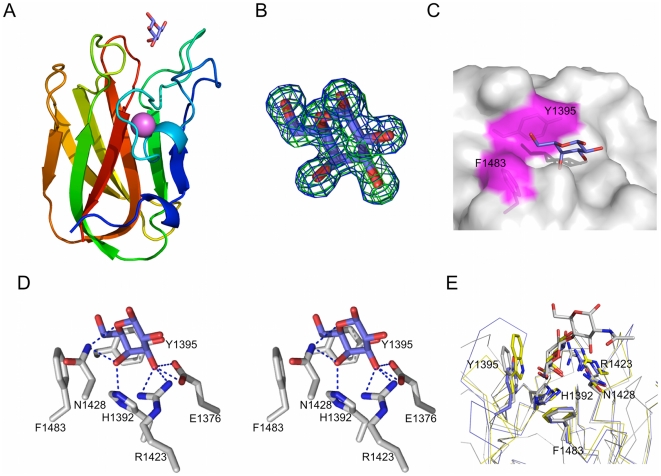
Figure 3. Structural analysis of the interaction between CBM32-5 and galactose.
(A) A cartoon representation of the structure of CBM32-5 bound to galactose (blue sticks) determined by X-ray crystallography to 1.55 Å resolution. The bound calcium atom is shown as a pink sphere. (B) Electron density for galactose within the binding site of CBM32-5. Electron density maps are maximum-likelihood/σA [59] -weighted 2F obs-F calc contoured at 1 σ (both maps at 0.45 e−/Å3) produced by refinements prior to modeling the sugar (green) and with the monosaccharide included (blue). (C) Surface representation of the CBM32-5 binding site with the bound galactose shown as blue sticks. The aromatic amino acids providing the hydrophobic binding platform are shown as sticks and labeled while the surface they contribute to the active site is coloured magenta. (D) Divergent stereo view of the key interactions between the binding site of CBM32-5 and galactose. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed black lines. (E) Comparison of the binding site of CBM32-5 (blue) with the CBM32 from C. perfringens GH84C (grey; PDB code 2J1E) and the CBM32 from C. perfringens NanJ (yellow; PDB code 2V72) reveals the canonical galactose-binding site. Conserved amino acid side chains and bound carbohydrates are shown as sticks.