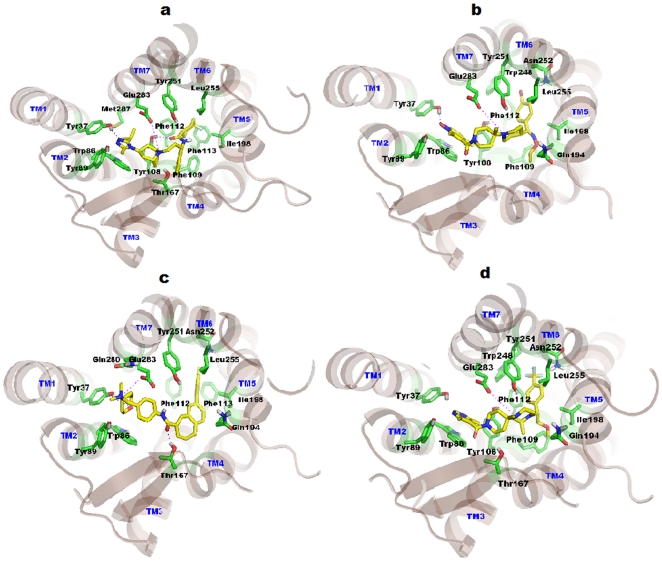
Figure 8. Binding modes of CCR5 inhibitors.
TM helices are shown in light brown color, whereas constructed binding pocket residues were shown in green sticks. All the TM's are labeled by blue color on the top of helices. Docked ligands were shown in yellow color. (a) Docked pose of Maraviroc in CCR5, the key salt bridge interaction with Glu283 is shown by magenta dotted line. Hydrogen bonds with Try37 and Tyr108 were shown in blue dotted lines. (b) Docking model of SCH-C show a key salt bridge interaction with Glu283 and represented by magenta dotted line. Hydrogen bond with Try37 is shown as blue dotted lines. Pyridine-N-Oxide ring of ligand interacts through strong aromatic π-stacking interaction with the Trp86 of CCR5. (c) TAK779 in CCR5 shows salt bridge interaction with Glu283 which is designated by magenta dotted line. Hydrogen bonds with Try37 and Thr167 are shown in blue dotted lines. Phenyl group of TAK779 docked deeply inside the cavity formed by Ile198, Tyr251, Asn252 and Leu255. (d) Docking model of Vicriviroc shows salt bridge interaction with Glu283 which is indicated by magenta dotted line. Pyrimidine ring of ligand interacts strongly via π-stacking interaction with Trp86. Tri-fluoro-phenyl of ligand is docked deeply into the cavity formed by Phe112, Ile198, Trp248, Tyr251, Asn252 and Leu255 residues.