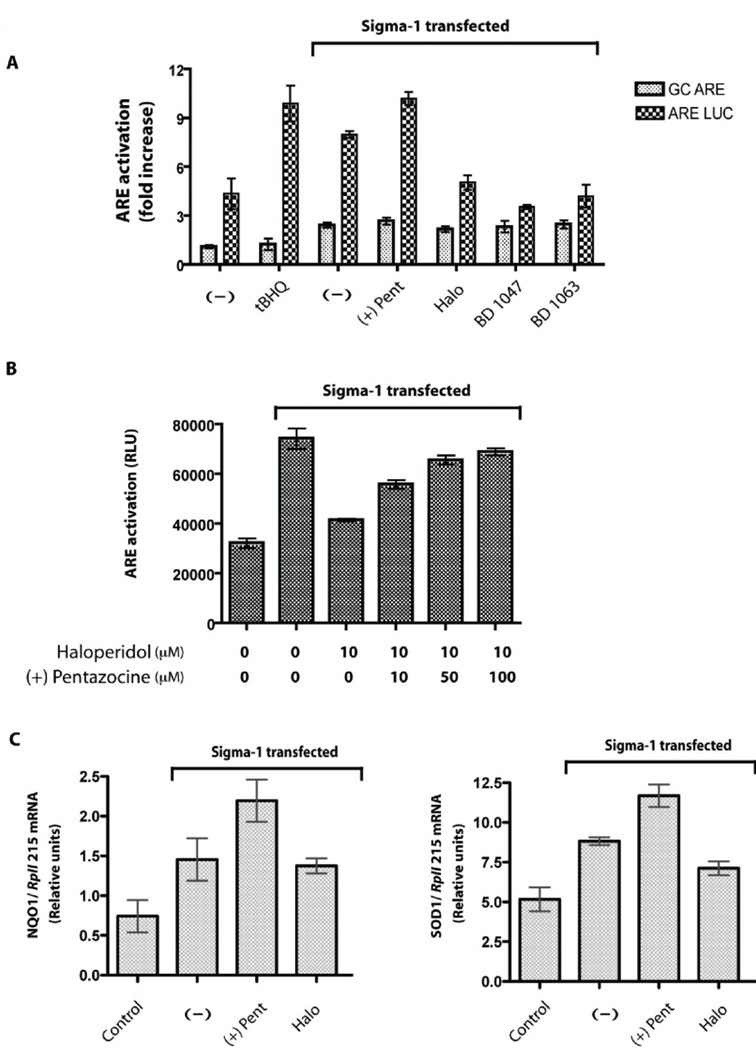
Figure 5. Sigma-1 receptor activates ‘Antioxidant Response Elements’ (ARE).
A. ARE activation by the sigma-1 receptors and its ligands in COS-7 cells (approximately 1×106 cells) using a luciferase reporter gene assay. Specificity of ARE activation was determined by using mutant GC-ARE luciferase construct, which is not activated by the known ARE activator, tertiary butyl hydroquinone (t-BHQ). Transfections of sigma-1 receptor in COS-7 cells showed almost a two fold specific ARE activation compared to that of the vehicle transfected COS-7 cells. The sigma-1 receptor agonist (+)-pentazocine (10 µM) showed a further increase in the specific ARE activation compared to that no drug treatment [(−) condition], whereas the antagonists haloperidol, BD 1047, and BD 1063 lowered the specific ARE activation. Error bars represent mean ± S.E.M. from three separate experiments (n = 3).
B. Reversal of haloperidol-mediated antagonism of ARE activation (n = 3). COS-7 cells transfected with guinea pig sigma-1 receptor (approximately 1×106 cells) were treated with 10 µM of haloperidol for 24 hours 2 days after transfection and lowered ARE activation was observed. Co-treatment of 50–100 µM (+)-pentazocine, a sigma-1 receptor agonist, reversed the antagonism shown by 10 µM of haloperidol. Error bars represent mean ± S.E.M. from different experiments (n = 3).
C. Real-time RT-PCR analysis of NQO1 and SOD1 mRNAs - the gene products which are under control of the ARE enhancer, in COS-7 cells. Transfection of sigma-1 receptor alone increased the SOD1 and NQO1 mRNA levels almost two fold compared to that of vehicle transfected condition (control) (n = 4). Treatment with the sigma-1 receptor agonist (+)-pentazocine (10 µM) showed a further increase in the NQO1 and SOD1 mRNA levels compared to the no drug treatment condition whereas the treatment of the antagonist haloperidol (10 µM) showed reverse effects. Error bars represent mean ± S.E.M. from four separate experiments (n = 4).