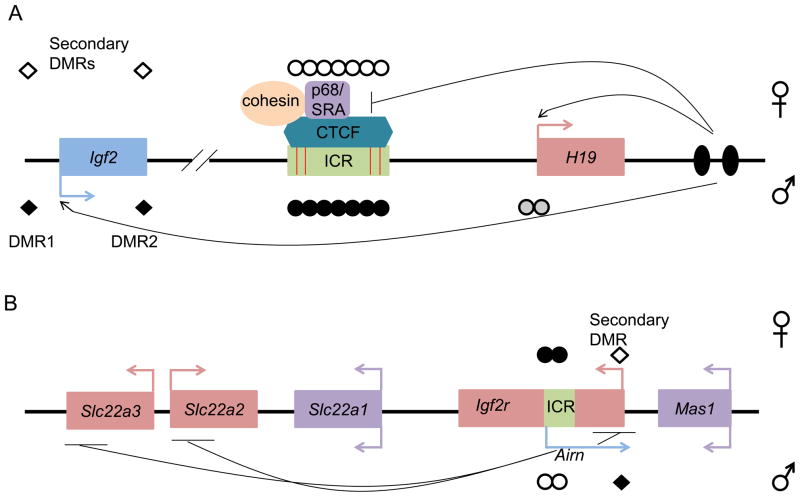
Figure 2. Depiction of insulator and ncRNA mediated imprinting.
(a) Insulator-mediated imprinting at the H19/Igf2 locus. The maternal allele is represented above the line whereas the paternal allele is below the line. Depicted here are the maternally expressed H19 (pink box with pink arrow) and paternally expressed Igf2 (blue box with blue arrow) genes. On the maternal allele the ICR (green box) remains unmethylated (open circles) allowing CTCF (binding sites depicted by red bars) and its cofactors (cohesins and p68/SRA) to bind. This interaction mediates enhancer blocking allowing downstream enhancers (black ovals) to access the H19 promoter. Paternal methylation at the ICR (black circles) prevents CTCF binding and together with methylation at the H19 promoter (grey circles) allows the enhancers to access Igf2. Paternal methylation at secondary DMRs (diamonds), DMR1 and DMR2, occurs after fertilization. (b) ncRNA-mediated imprinting at the Igf2r locus. The maternal allele is represented above the line whereas the paternal allele is below the line. Depicted are the maternally expressed Slc22a3, Slc22a2, Igf2r (pink boxes with pink arrows) the paternally expressed ncRNA Airn (blue arrow) and non-imprinted Mas1 and Slc22a1 (purple boxes with purple arrows). The ICR (green box), which is hypermethylated on the maternal allele (black circles), includes the Airn promoter. The hypomethylated ICR (open circles) on the paternal allele allows Airn expression, which represses Slc222a2, Slc22a3 and Igf2r in cis. A secondary paternally methylated DMR (diamonds) is located at the Igf2r promoter. This DMR is not methylated until after transcription occurs through the region. Loci are not drawn to scale.