Fig. 2.
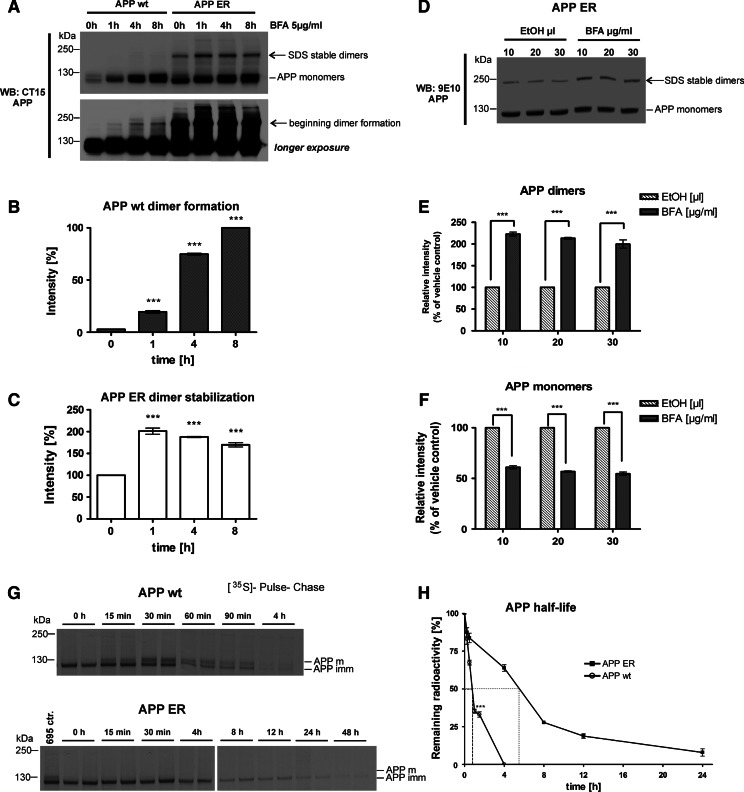
Homodimerization of APP wt can be induced by inhibiting protein traffic out of the ER with brefeldin A. a CHO-K1 cells stably overexpressing either APP695 wt or APP695 fused to the ER retention motif KKAA (APP695 ER) were treated with 5 μg/ml brefeldin A (BFA) for the indicated time points (0–8 h). Aliquots of cell lysates were mixed with SDS sample buffer, containing BME without heat denaturing and separated on a 4–12% SDS-PAGE. APP was detected with CT15 antibody, shown on one representative Western blot. The bottom panel shows a longer exposure time, indicating dimer formation of APP695 wt when export of the ER is blocked by BFA. b Diagram showing the ratio of APP wt dimer formation during BFA treatment, plotted against time, with ± SEM of three independent experiments, statistical significance: ***p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA. c Diagram depicting increasing stabilization of APP ER preexisting dimers during BFA treatment, plotted against time. Data represent ± SEM (n ≥ 3), statistical significance: ***p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA. d Cell cultures of CHO-K1 overexpressing APP ER were treated for 1 h with increasing concentrations (10–30 μg) of BFA, or with vehicle (100% ethanol) alone. Samples were treated as under a. APP was detected with monoclonal 9E10 antibody, shown as one representative Western blot. e Diagram showing relative increase of APP ER dimers with higher BFA concentrations, quantified as percentage over vehicle control. Data represent ± SEM as indicated (n ≥ 3). Statistical significance: ***p < 0.001, t test. f Diagram showing simultaneous reduction of APP monomers with increasing BFA concentrations, depicted as percentage of vehicle control. Data represent ± SEM as indicated (n ≥ 3). Statistical significance: ***p < 0.001, t test. g ER retention inhibits APP degradation and increases its half-life. CHO-K1 cell cultures stably overexpressing either APP695 wt or APP695 ER, respectively, were pulse-labeled for 15 min with 150 μCi of [35S] methionine/cysteine. Cells were harvested immediately after the pulse (0 min), or chased for the indicated time points with non-radioactive medium. APP was immunoprecipitated with monoclonal 9E10 antibody and subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by autoradiography on an X-ray film for a minimum of 16 h at −80°C. Note that different time points for APP695 ER were chosen due to its extended half-life. APP mature (APP m) and immature form (APP imm) are indicated. All time points were run in duplicates. For APP ER, samples were run alongside an APP wt control sample to confirm the difference between immature and mature APP. h Half-life graph. Data are mean ± SEM of four independent experiments. *** Statistically significant difference (p < 0.001; t test) between APP wt and APP ER is indicated