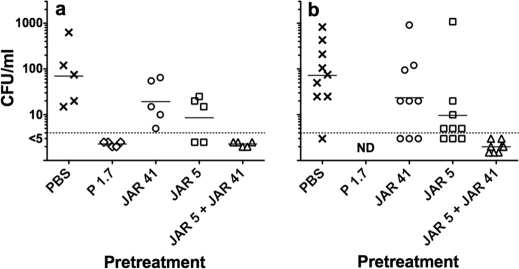
Figure 6. JAR 41 augments passive protective activity of anti-fHbp mAb JAR 5 against bacteremia caused by group B strain H44/76 in human fH transgenic infant rats.
Panel a, Experiment 1, 8- to 9-day old rats challenged IP with 4900 CFU/rat; Panel b, Experiment 2, 6- to 7-day old rats challenged IP with 760 CFU/rat. In both experiments, rats were given a total dose of 25 µg of mAb or phosphate buffered saline alone (PBS, negative control) 1 hr before the bacterial challenges. The combination contained 12.5 µg of each mAb. Blood cultures were obtained 6 hrs after challenge. Compared to PBS, rats given JAR 5 alone had a lower geometric mean CFU/ml (Experiment 1, p = 0.04 and Experiment 2, p<0.03)) but there was no protection by JAR 41 alone (p>0.05). In Experiment 2, the combination of JAR 41 and JAR 5 (0/8 with bacteremia) had greater protective activity than JAR 5 alone (6 out of 9 with bacteremia, p = 0.009, Fisher's exact test). ND, not done.