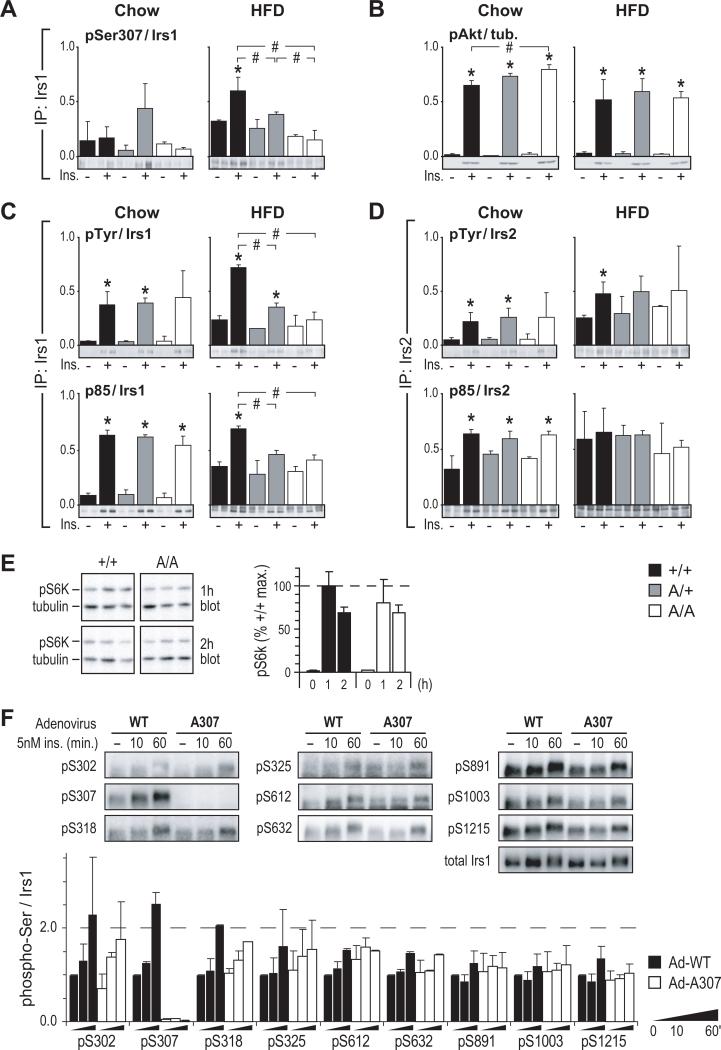
Figure 3. Mutation of Ser307 Fails To Protect Against HFD-Induced Desensitization of Insulin Signaling.
(A) Immunoblot analysis of basal (–) and insulin-stimulated (+) Ser307 phosphorylation in hindlimb muscle of 5 to 6-month-old mice fed chow (Chow) or high-fat diet (HFD). Immunoprecipitated Irs1 (IP: Irs1) was detected using a phospho-specific antibody against 15 residues of mouse Irs1.
(B) Corresponding Akt (Thr308) phosphorylation.
(C-D) Immunoprecipitation (IP:) and immunoblot analysis of insulin signaling by Irs1 (C) or Irs2 (D) in muscle of chow- and HFD-fed mice; pTyr: phosphotyrosine.
In panels A-D, the estimated means of phosphotyrosine, p85, or phospho-Thr308Akt signals (see methods) were normalized to the average total Irs1, Irs2, or tubulin concentrations;
* = significant difference (Bonferroni p<0.05) vs. unstimulated; # = significant difference (Bonferroni p<0.05) between indicated insulin-stimulated samples.
(E) Immunoblot analysis of p70 S6 kinase (Thr389) phosphorylation (mean ± SEM) in livers of overnight fasted mice re-fed for 1 or 2 h. Mice were previously fed chow diet.
(F) Immunoblot analysis of Irs1 Ser/Thr phosphorylation. Primary hepatocytes from mice lacking hepatic Irs1 and Irs2 (‘LDKO’ Dong et al., 2008) were infected with wild-type (Ad-WT) or mutant (Ad-A307) Irs1 adenovirus for 24 h, then treated as shown after 16 h of serum starvation. Relative Irs1 phosphorylation (mean ± SEM) at each site is graphed as fold of Ad-WT-infected cells without insulin (–).