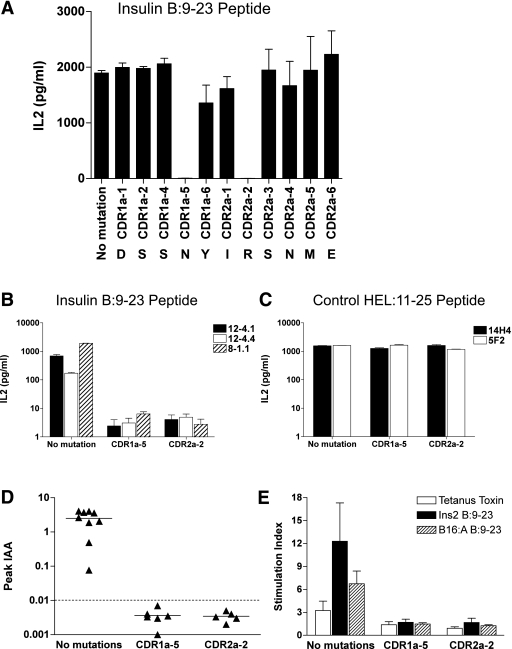
FIG. 5.
Two amino acid residues at CDR1 and CDR2 of Vα TRAV5D-4 are essential for the recognition of insulin B:9–23 and anti-insulin autoimmunity induced by Vα TRAV5D-4. A: Alanine scan of the 8–1.1 insulin B:9–23-reactive TCR. 5KC cells expressing the 8–1.1 TCR with alanine mutations at individual CDRα positions were tested for the IL2 secretion in response to insulin B:9–23 peptide. Reactivity was lost only when CDR1α-5 and CDR2α-2 were mutated to alanine. Data are mean ± SEM and cumulative from two independent experiments. 5KC cells expressing TCRs (B: insulin B:9–23-reactive TCRs; C: HEL:11–25-reactive TCRs) with or without an alanine mutation at position CDR1α-5 or CDR2α-2 were tested for the IL-2 secretion in response to insulin B:9–23 (B) or HEL:11–25 (C). All three insulin B:9–23-reactive TCRs lost reactivity with these mutations, whereas anti-HEL peptide response by two HEL:11–25-reactive TCRs was unaffected. Data are mean ± SEM and cumulative from equal to or greater than three independent experiments. D: Insulin autoantibodies of mice retrogenic for 8–1.1 α-chain with or without alanine mutation at CDR1α-5 or CDR2α-2. Equal to or greater than five mice per individual strains were bled to measure insulin autoantibodies every 4 weeks between 4 and 16 weeks after bone marrow transplantation. Symbols represent individual mice. IAA index ≥0.01 is defined as positive. E: Spleen cells from mice retrogenic for 8–1.1 insulin B:9–23-reactive α-chain with or without an alanine mutation at CDR1α-5 or CDR2α-2 were tested for IFN-γ response to tetanus toxin peptide 830–843 (open bar), insulin B:9–23 peptide (closed bar), and B16:A B:9–23 peptide (hatched bar) by IFN-γ ELISPOT assay. Data are mean ± SEM and are cumulative from equal to or greater than three independent experiments. Stimulation Index >3 is considered positive.